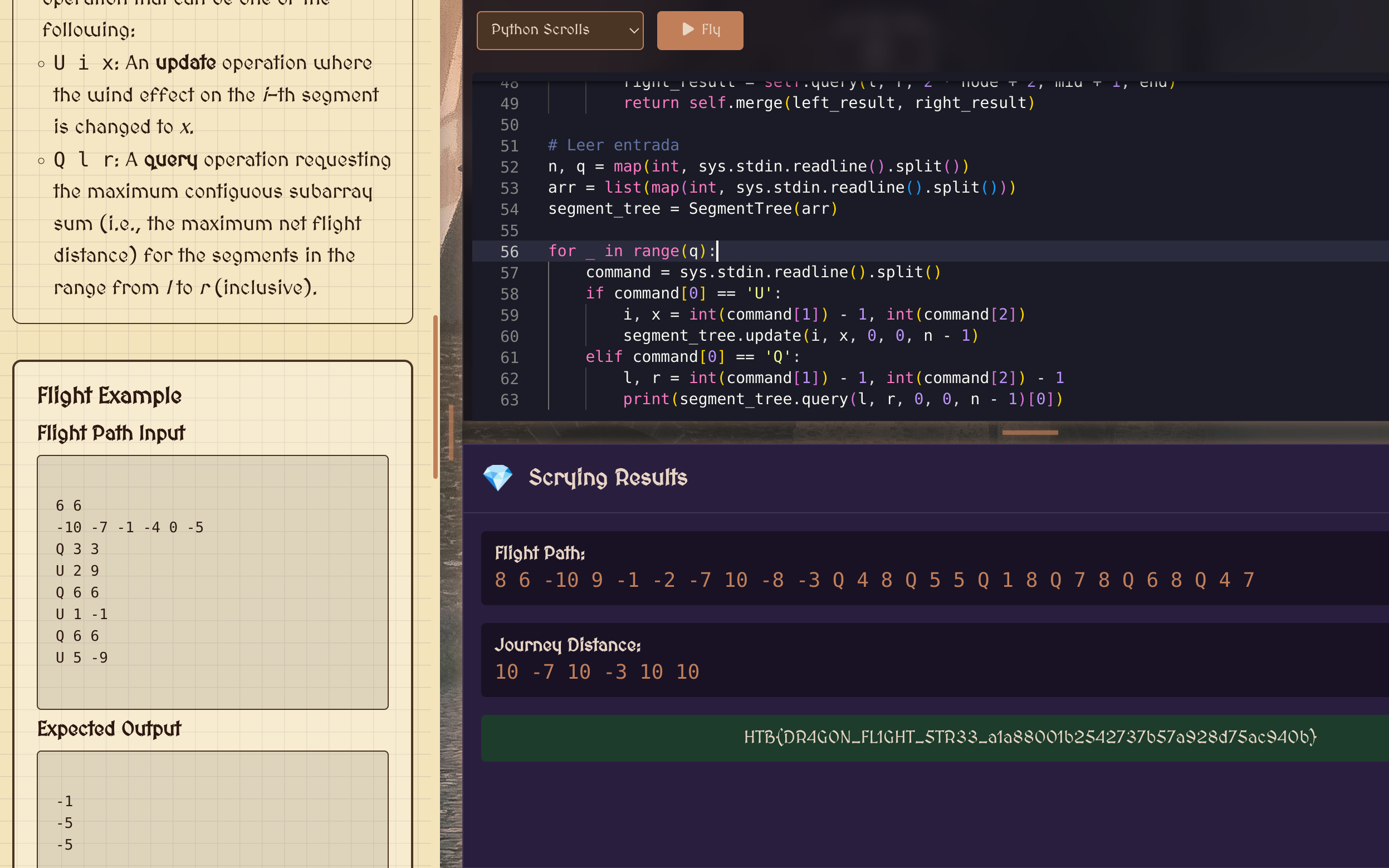
Segment Tree + Kadane’s Algorithm
Explanation:
- Two types of operations were required:
- Updating wind values at a given index (
U i x), which suggests efficient data structures like a Segment Tree or Fenwick Tree. - Querying the maximum contiguous subarray sum (
Q l r), which is a classic problem solved using Kadane’s Algorithm.
- Updating wind values at a given index (
- Using a Segment Tree, we optimized both operations:
- Updates: O(log N) time complexity instead of O(N).
- Queries: O(1) with Kadane’s Algorithm.
import sys
class SegmentTree:
def __init__(self, arr):
self.n = len(arr)
self.tree = [(-float('inf'), 0, -float('inf'), -float('inf'))] * (4 * self.n)
self.build(arr, 0, 0, self.n - 1)
def build(self, arr, node, start, end):
if start == end:
value = arr[start]
self.tree[node] = (value, value, value, value) # (max_sum, total_sum, best_prefix, best_suffix)
else:
mid = (start + end) // 2
left_child = 2 * node + 1
right_child = 2 * node + 2
self.build(arr, left_child, start, mid)
self.build(arr, right_child, mid + 1, end)
self.tree[node] = self.merge(self.tree[left_child], self.tree[right_child])
def merge(self, left, right):
max_sum = max(left[0], right[0], left[3] + right[2])
total_sum = left[1] + right[1]
best_prefix = max(left[2], left[1] + right[2])
best_suffix = max(right[3], right[1] + left[3])
return (max_sum, total_sum, best_prefix, best_suffix)
def update(self, idx, value, node, start, end):
if start == end:
self.tree[node] = (value, value, value, value)
else:
mid = (start + end) // 2
left_child = 2 * node + 1
right_child = 2 * node + 2
if idx <= mid:
self.update(idx, value, left_child, start, mid)
else:
self.update(idx, value, right_child, mid + 1, end)
self.tree[node] = self.merge(self.tree[left_child], self.tree[right_child])
def query(self, l, r, node, start, end):
if r < start or l > end:
return (-float('inf'), 0, -float('inf'), -float('inf'))
if l <= start and end <= r:
return self.tree[node]
mid = (start + end) // 2
left_result = self.query(l, r, 2 * node + 1, start, mid)
right_result = self.query(l, r, 2 * node + 2, mid + 1, end)
return self.merge(left_result, right_result)
# Leer entrada
n, q = map(int, sys.stdin.readline().split())
arr = list(map(int, sys.stdin.readline().split()))
segment_tree = SegmentTree(arr)
for _ in range(q):
command = sys.stdin.readline().split()
if command[0] == 'U':
i, x = int(command[1]) - 1, int(command[2])
segment_tree.update(i, x, 0, 0, n - 1)
elif command[0] == 'Q':
l, r = int(command[1]) - 1, int(command[2]) - 1
print(segment_tree.query(l, r, 0, 0, n - 1)[0])