Once arriving onto an unknown network, our first goal is to identify where we are and what we can get to. During the red team engagement, we need to understand what target system we are dealing with, what service the machine provides, what kind of network we are in. Thus, the enumeration of the compromised machine after getting initial access is the key to answering these questions. This task will discuss the common types of networks we may face during the engagement.
Network segmentation is an extra layer of network security divided into multiple subnets. It is used to improve the security and management of the network. For example, it is used for preventing unauthorized access to corporate most valuable assets such as customer data, financial records, etc.
The Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) is a network technique used in network segmentation to control networking issues, such as broadcasting issues in the local network, and improve security. Hosts within the VLAN can only communicate with other hosts in the same VLAN network.
If you want to learn more about network fundamentals, we suggest trying the following TryHackMe module: Network Fundamentals.
Internal Networks
Internal Networks are subnetworks that are segmented and separated based on the importance of the internal device or the importance of the accessibility of its data. The main purpose of the internal network(s) is to share information, faster and easier communications, collaboration tools, operational systems, and network services within an organization. In a corporate network, the network administrators intend to use network segmentation for various reasons, including controlling network traffic, optimizing network performance, and improving security posture.
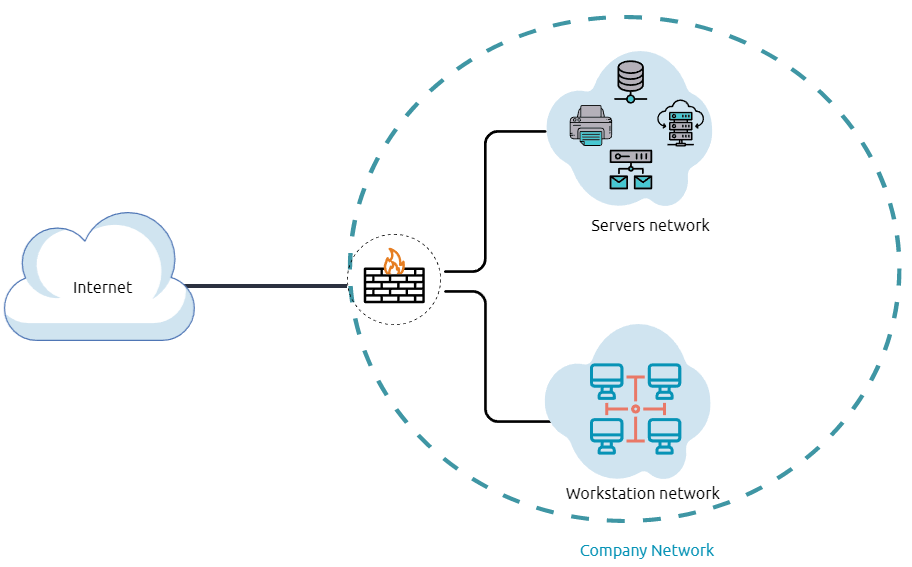
The previous diagram is an example of the simple concept of network segmentation as the network is divided into two networks. The first one is for employee workstations and personal devices. The second is for private and internal network devices that provide internal services such as DNS, internal web, email services, etc.
A Demilitarized Zone (DMZ)
A DMZ Network is an edge network that protects and adds an extra security layer to a corporation’s internal local-area network from untrusted traffic. A common design for DMZ is a subnetwork that sits between the public internet and internal networks.
Designing a network within the company depends on its requirements and need. For example, suppose a company provides public services such as a website, DNS, FTP, Proxy, VPN, etc. In that case, they may design a DMZ network to isolate and enable access control on the public network traffic, untrusted traffic.
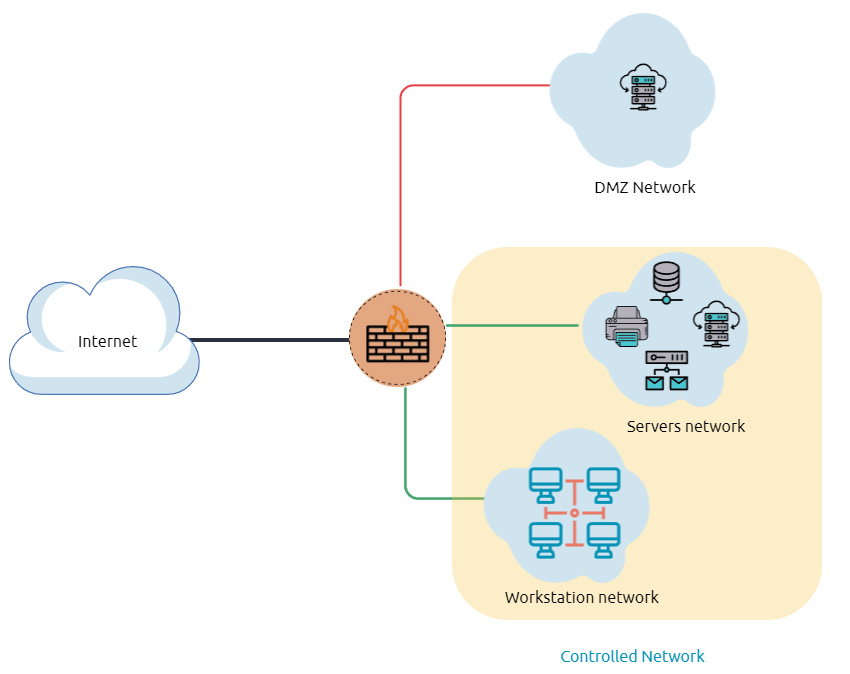
In the previous diagram, we represent the network traffic to the DMZ network in red color, which is untrusted ( comes directly from the internet). The green network traffic between the internal network is the controlled traffic that may go through one or more than one network security device(s).
Enumerating the system and the internal network is the discovering stage, which allows the attacker to learn about the system and the internal network. Based on the gained information, we use it to process lateral movement or privilege escalation to gain more privilege on the system or the AD environment.
Network Enumeration
There are various things to check related to networking aspects such as TCP and UDP ports and established connections, routing tables, ARP tables, etc.
Let’s start checking the target machine’s TCP and UDP open ports. This can be done using the netstat command as shown below.
PS C:\Users\thm> netstat -na
Active Connections
Proto Local Address Foreign Address State
TCP 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING
TCP 0.0.0.0:88 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING
TCP 0.0.0.0:135 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING
TCP 0.0.0.0:389 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENINGThe output reveals the open ports as well as the established connections. Next, let’s list the ARP table, which contains the IP address and the physical address of the computers that communicated with the target machines within the network. This could be helpful to see the communications within the network to scan the other machines for open ports and vulnerabilities.
PS C:\Users\thm> arp -a
Interface: 10.10.141.51 --- 0xa
Internet Address Physical Address Type
10.10.0.1 02-c8-85-b5-5a-aa dynamic
10.10.255.255 ff-ff-ff-ff-ff-ff staticInternal Network Services
It provides private and internal network communication access for internal network devices. An example of network services is an internal DNS, web servers, custom applications, etc. It is important to note that the internal network services are not accessible outside the network. However, once we have initial access to one of the networks that access these network services, they will be reachable and available for communications.
We will discuss more Windows applications and services in Task 9, including DNS and custom web applications.
NOTE: A DMZ or demilitarized zone is a perimeter network that protects and adds an extra layer of security to an organization’s internal local-area network from untrusted traffic. The end goal of a demilitarized zone network is to allow an organization to access untrusted networks, such as the internet, while ensuring its private network or LAN remains secure
NOTE: Active Directory is a directory service developed by Microsoft for Windows domain networks. It stores information about network objects such as computers, users, and groups. It provides authentication and authorisation services, and allows administrators to manage network resources centrally.
NOTE: Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is responsible for finding the MAC (hardware) address related to a specific IP address. It works by broadcasting an ARP query, “Who has this IP address? Tell me.” And the response is of the form, “The IP address is at this MAC address.”
