- Open an empty directoy
- Open a terminal and run
npm init -y. This will generate a package.json - Install express:
npm install express --safe. This will generate a package-lock.json and a folder called node-modules - Create an
index.js
const express = require("express"); //load express library
const app = express(); //express app initializing- Create a hello world program:
const express = require("express"); //load express library
const app = express(); //express app initializing
//petition get to the root directory, 2nd param is callback function
app.get("/", (reequest, response) => {
//we have to set what we're going to do with response and request
return response.send("Hello world!"); //prints hello world
});
//Port listening the inbound traffic
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log("App running on http://localhost:3000");
});- Create a new folder called store (for databases)
- Continue developing the app to read data from a json file:
const express = require("express"); //load express library
const fs = require("fs"); //library fileSystem for access information stored
const app = express(); //express app initializing
//petition get to the root directory, 2nd param is callback function
app.get("/", (request, response) => {
//we have to set what we're going to do with response and request
return response.send("Hello world!"); //prints hello world
});
//Create an endpoint
app.get("/todos", (request, response) => {
//To read the file we stored on store directory with utf-8 encoding
//Last parameter is the callback function
fs.readFile("./store/todos.json", "utf-8", (err, data) => {
//Handling errors
if (err) {
return response.status(500).send("Something went wrong :("); //http code 500 (error) with a special message
} //the next code will not execute
//We are parsing data to JSON because data is actually a string
const todos = JSON.parse(data);
return response.json({ todos: todos }); //we return a list like the todos.json
});
});
//Port listening the inbound traffic
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log("App running on http://localhost:3000");
});Now check the localhost:3000/todos url 8. Download Postman 9. Create a get petition to the localhost:3000/todos url 10. Remember that express treats const as strings always. Types are very important so make sure your types are correct. 11. Add modify functionality:
const express = require("express"); //load express library
const fs = require("fs"); //library fileSystem for access information stored
const app = express(); //express app initializing
//petition get to the root directory, 2nd param is callback function
app.get("/", (request, response) => {
//we have to set what we're going to do with response and request
return response.send("Hello world!"); //prints hello world
});
//Create an endpoint
app.get("/todos", (request, response) => {
//To read the file we stored on store directory with utf-8 encoding
//Last parameter is the callback function
fs.readFile("./store/todos.json", "utf-8", (err, data) => {
//Handling errors
if (err) {
return response.status(500).send("Something went wrong :("); //http code 500 (error) with a special message
} //the next code will not execute
//We are parsing data to JSON because data is actually a string
const todos = JSON.parse(data);
return response.json({ todos: todos }); //we return a list like the todos.json
});
});
//To complete todos on the list
app.put("/todos/:id/complete", (request, response) => {
const id = request.params.id; //The id of the todo
//function that finds a todo by its id
const findTodoById = (todos, id) => {
//go through the items of the todos list
for (let i = 0; i < todos.length; i++) {
if (todos[i].id === parseInt(id)) {
//parseInt necessary because express treats const as strings by default
//if the element's id coincides
return i;
}
}
return -1; //if not found
};
//To change the value on the file
fs.readFile("./store/todos.json", "utf-8", (err, data) => {
//Handling errors
if (err) {
return response.status(500).send("Something went wrong :("); //http code 500 (error) with a special message
} //the next code will not execute
//We are parsing data to JSON because data is actually a string
const todos = JSON.parse(data);
const todoIndex = findTodoById(todos, id);
if (todoIndex == -1) {
return response.status(404).send("File not found");
}
return response.json(todos[todoIndex]);
});
}); //quick request to mark a todo
//Port listening the inbound traffic
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log("App running on http://localhost:3000");
});- Add save to a file functionality:
const express = require("express"); //load express library
const fs = require("fs"); //library fileSystem for access information stored
const app = express(); //express app initializing
//petition get to the root directory, 2nd param is callback function
app.get("/", (request, response) => {
//we have to set what we're going to do with response and request
return response.send("Hello world!"); //prints hello world
});
//Create an endpoint
app.get("/todos", (request, response) => {
//To read the file we stored on store directory with utf-8 encoding
//Last parameter is the callback function
fs.readFile("./store/todos.json", "utf-8", (err, data) => {
//Handling errors
if (err) {
return response.status(500).send("Something went wrong :("); //http code 500 (error) with a special message
} //the next code will not execute
//We are parsing data to JSON because data is actually a string
const todos = JSON.parse(data);
return response.json({ todos: todos }); //we return a list like the todos.json
});
});
//To complete todos on the list
app.put("/todos/:id/complete", (request, response) => {
const id = request.params.id; //The id of the todo
//function that finds a todo by its id
const findTodoById = (todos, id) => {
//go through the items of the todos list
for (let i = 0; i < todos.length; i++) {
if (todos[i].id === parseInt(id)) {
//parseInt necessary because express treats const as strings by default
//if the element's id coincides
return i;
}
}
return -1; //if not found
};
//To change the value on the file
fs.readFile("./store/todos.json", "utf-8", (err, data) => {
//Handling errors
if (err) {
return response.status(500).send("Something went wrong :("); //http code 500 (error) with a special message
} //the next code will not execute
//We are parsing data to JSON because data is actually a string
let todos = JSON.parse(data); //let allow to modify the content (different from const)
const todoIndex = findTodoById(todos, id);
if (todoIndex == -1) {
return response.status(404).send("File not found");
}
todos[todoIndex].complete = true; //we put the value as true
//we write changes to the file with todos data being stringify (converted back to)
fs.writeFile("./store/todos.json", JSON.stringify(todos), () => {
return response.json({ status: "ok" });
});
});
}); //quick request to mark a todo
//Port listening the inbound traffic
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log("App running on http://localhost:3000");
});- Now we apply a filter:
const express = require("express"); //load express library
const fs = require("fs"); //library fileSystem for access information stored
const app = express(); //express app initializing
//petition get to the root directory, 2nd param is callback function
app.get("/", (request, response) => {
//we have to set what we're going to do with response and request
return response.send("Hello world!"); //prints hello world
});
//Create an endpoint
app.get("/todos", (request, response) => {
//filter all the complete todos ones
const showPending = request.query.showpending;
//To read the file we stored on store directory with utf-8 encoding
//Last parameter is the callback function
fs.readFile("./store/todos.json", "utf-8", (err, data) => {
//Handling errors
if (err) {
return response.status(500).send("Something went wrong :("); //http code 500 (error) with a special message
} //the next code will not execute
//We are parsing data to JSON because data is actually a string
const todos = JSON.parse(data);
//if the query paramenter showpending is not equals to the string "1"
if (showPending !== "1") {
return response.json({ todos: todos }); //we return a list like the todos.json
} else {
//filter them (return only those which are not completed)
return response.json({
todos: todos.filter((t) => {
return t.complete === false;
}),
});
}
});
});
//To complete todos on the list
app.put("/todos/:id/complete", (request, response) => {
const id = request.params.id; //The id of the todo
//function that finds a todo by its id
const findTodoById = (todos, id) => {
//go through the items of the todos list
for (let i = 0; i < todos.length; i++) {
if (todos[i].id === parseInt(id)) {
//parseInt necessary because express treats const as strings by default
//if the element's id coincides
return i;
}
}
return -1; //if not found
};
//To change the value on the file
fs.readFile("./store/todos.json", "utf-8", (err, data) => {
//Handling errors
if (err) {
return response.status(500).send("Something went wrong :("); //http code 500 (error) with a special message
} //the next code will not execute
//We are parsing data to JSON because data is actually a string
let todos = JSON.parse(data); //let allow to modify the content (different from const)
const todoIndex = findTodoById(todos, id);
if (todoIndex == -1) {
return response.status(404).send("File not found");
}
todos[todoIndex].complete = true; //we put the value as true
//we write changes to the file with todos data being stringify (converted back to)
fs.writeFile("./store/todos.json", JSON.stringify(todos), () => {
return response.json({ status: "ok" }); //we return ok as it has been modified
});
});
}); //quick request to mark a todo
//Port listening the inbound traffic
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log("App running on http://localhost:3000");
});- To add items via post requests:
const express = require("express"); //load express library
const fs = require("fs"); //library fileSystem for access information stored
const app = express(); //express app initializing
//for adding items with post requests
app.use(express.json());
app.use(express.urlencoded({ extended: true }));
//petition get to the root directory, 2nd param is callback function
app.get("/", (request, response) => {
//we have to set what we're going to do with response and request
return response.send("Hello world!"); //prints hello world
});
//Create an endpoint
app.get("/todos", (request, response) => {
//filter all the complete todos ones
const showPending = request.query.showpending;
//To read the file we stored on store directory with utf-8 encoding
//Last parameter is the callback function
fs.readFile("./store/todos.json", "utf-8", (err, data) => {
//Handling errors
if (err) {
return response.status(500).send("Something went wrong :("); //http code 500 (error) with a special message
} //the next code will not execute
//We are parsing data to JSON because data is actually a string
const todos = JSON.parse(data);
//if the query paramenter showpending is not equals to the string "1"
if (showPending !== "1") {
return response.json({ todos: todos }); //we return a list like the todos.json
} else {
//filter them (return only those which are not completed)
return response.json({
todos: todos.filter((t) => {
return t.complete === false;
}),
});
}
});
});
//To complete todos on the list
app.put("/todos/:id/complete", (request, response) => {
const id = request.params.id; //The id of the todo
//function that finds a todo by its id
const findTodoById = (todos, id) => {
//go through the items of the todos list
for (let i = 0; i < todos.length; i++) {
if (todos[i].id === parseInt(id)) {
//parseInt necessary because express treats const as strings by default
//if the element's id coincides
return i;
}
}
return -1; //if not found
};
//To change the value on the file
fs.readFile("./store/todos.json", "utf-8", (err, data) => {
//Handling errors
if (err) {
return response.status(500).send("Something went wrong :("); //http code 500 (error) with a special message
} //the next code will not execute
//We are parsing data to JSON because data is actually a string
let todos = JSON.parse(data); //let allow to modify the content (different from const)
const todoIndex = findTodoById(todos, id);
if (todoIndex == -1) {
return response.status(404).send("File not found");
}
todos[todoIndex].complete = true; //we put the value as true
//we write changes to the file with todos data being stringify (converted back to)
fs.writeFile("./store/todos.json", JSON.stringify(todos), () => {
return response.json({ status: "ok" }); //we return ok as it has been modified
});
});
}); //quick request to mark a todo
//add items with post requests
app.post("/todo", (request, response) => {
if (!request.body.name) {
return response.status(400).send("Missing name");
}
fs.readFile("./store/todos.json", "utf-8", (err, data) => {
//Handling errors
if (err) {
return response.status(500).send("Something went wrong :("); //http code 500 (error) with a special message
} //the next code will not execute
const todos = JSON.parse(data);
//We find the max id on the file
const maxId = Math.max.apply(
Math,
todos.map((t) => {
return t.id;
})
);
//We add a new value with a new id higher that higher obtained
todos.push({
id: maxId + 1,
complete: false,
name: request.body.name,
});
//Write changes to the file
fs.writeFile("./store/todos.json", JSON.stringify(todos), () => {
return response.json({ status: "ok" }); //we return ok as it has been modified
});
});
});
//Port listening the inbound traffic
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log("App running on http://localhost:3000");
});- To dockerize the app:
- Install Docker
- Open it (make sure it’s opened before doing anything)
- Create a new file called
Dockerfile, where instructions for docker will be descripted
# linux container
FROM node:12
# app directory
WORKDIR /app
# environment variable
ENV NODE_ENV production
# copy package logs files into the working directory
COPY package*.json ./
# docker will make npm install
RUN npm install
# copy all the sources files (from current paste into working directory)
COPY . .
# installs the library pm2
RUN npm install -g pm2
# expose the port 3000
EXPOSE 3000
# executes the library
CMD ["pm2-runtime", "index.js"]- Create a new file called
.dockerignoreand type this to ignore all the node packages:
node_modules- Go to the aws console an type (create a Elastic Container Repository):
- ecr >> repositories
- Create a new repository
- View push commands (execute them)
- Type ecs >> clusters (To create a Elastic Cluster) (make sure you use the old version)
- Do not click VPC
- Go to the tasks definitions of the new cluster:
- Create a new one with fargate
- Assign a name like
taskdef-xxx - Add a task size of 0.5 Gb and 0.25vCPU
- Click add container
- Put a name (maybe the same as the container you created before) like
container-xxx - On image copy the url of the repository where all was store (ecr)
- Go back to ecr
- Copy the image uri of your latest repository
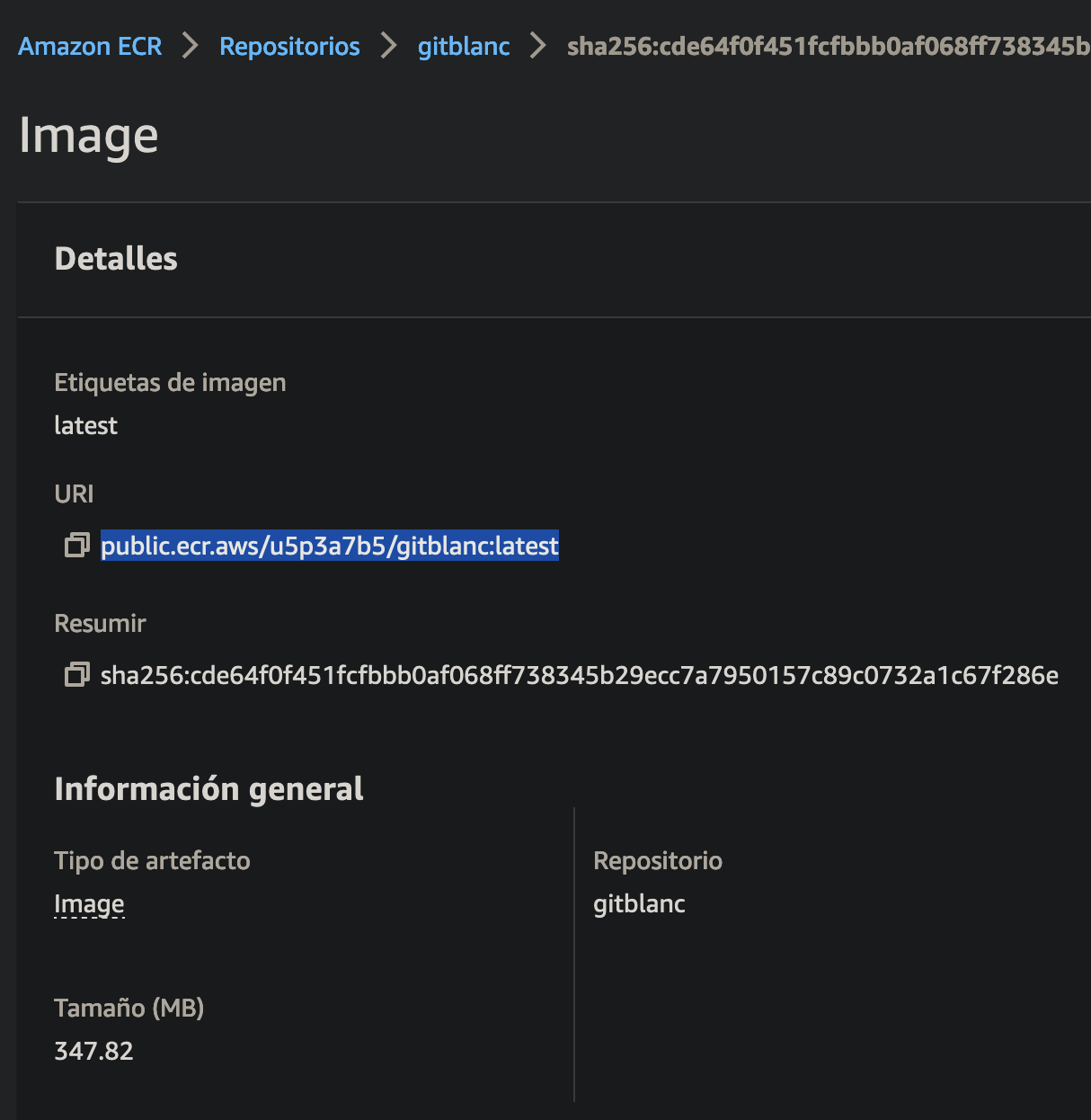
- Keep default soft Limit (128)
- Put port 3000 on port maps with protocol tcp
- Leave blank the rest and create
- Go to the cluster you created before >> Services:
- Create a new Service
- Select FARGATE
- select the latest task definition
- Add a task and a service name
- Leave the rest by default and click next
- Select the VPC of the cluster you want
- Add your subnets
- Edit security groups
- Select Custom TCP
- Put the port 3000
- Save
- Select Application Load Balancer
- Put health check period to 30
- Create an application load balancer
- Select the http/https one
- Give it a name like
alb-xxx - Listener set to HTTP on port 80 (Create a target group if not exists)
- Select the default vpc and select all the subnets
- Refresh the tasks view (1~2mis)
